Difference between revisions of "Mv mipi camera manual"
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
===== Rolling shutter ===== | ===== Rolling shutter ===== | ||
| − | In high-speed trigger mode, | + | In high-speed trigger mode, assume '''Trigger Number''' is N, frames 2-N are output immediately after the previous frame and there is no more trigger interval. This allows the same maximum frame rate to be achieved as in video streaming mode. |
===Image Feature=== | ===Image Feature=== | ||
Revision as of 14:56, 11 March 2022
MV series MIPI image module manual
1 Overview
MV series is a series of camera modules specially designed for machine vision. It is excellent in performance, compact and affordable in price. In addition to the video streaming mode, a trigger mode and a series of functions related to triggering are also provided. Provides a better option for embedded systems for machine vision applications.
To facilitate rapid development, we provide hardware datasheet , register manuals and drivers for embedded platforms, demos.
This article focuses on the functional principles of the MV camera in detail. For hardware manuals, registers, configuration scripts, drivers for different embedded platforms and usage, please refer to the corresponding documents.
In this article, the [Related Commands] column after each function lists the commands in the mv_mipi_i2c.sh script that are related to this function.
2 Image Acquisition
2.1 Rolling shutter and Global shutter
2.1.1 Rolling shutter
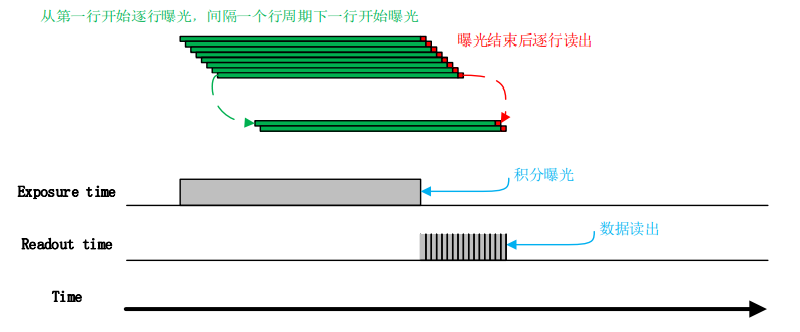
The rolling shutter sensor is implemented as shown in the figure below.。The exposure starts from the first line and the second line is exposed only after one line cycle.And so on, after N-1 rows the Nth row is exposed.It takes one cycle time to read out a row of data after the first row is exposed.After the first line is completely read out, the second line just starts to be read out. In this order, the whole image is completely read out. The rolling shutter sensors are less technically difficult than global exposure sensors, cheaper, and have greater resolution, making them a good choice for some static or slow object photography.
2.1.2 Global shutter
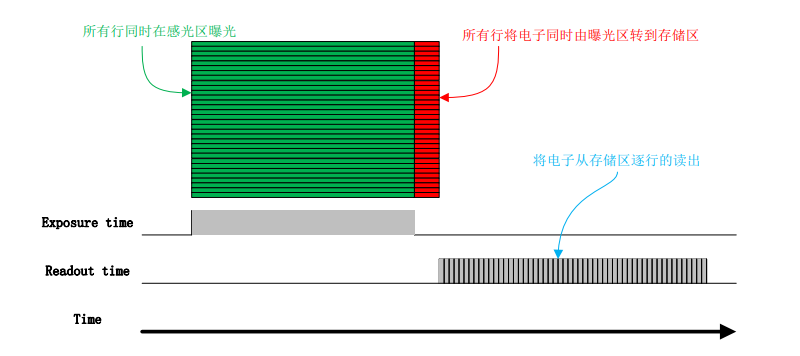
The global shutter sensor implementation is shown in the figure below. All rows of the sensor start exposure at the same time and end exposure at the same time. At the end of the exposure, the sensor transfers all electrons from the sensing area to the storage area and then reads out the pixel data row by row.The advantage of such exposure is that the image will not be shifted and skewed when shooting moving objects.
2.2 Start/Stop Acquisition
You can send the start acquisition and stop acquisition commands to the camera at any time.
Once the camera receives the start acquisition command, if working in video streaming mode, it will immediately start exposure and output images; if working in trigger mode, it will enter the state of waiting for the trigger signal. At the same time, the camera enters the running state.
Once the camera receives the stop capture command, it will complete the currently transmitting frames to ensure frame integrity, and then stop outputting images and enter the standby state. Note that the triggering process will be interrupted if triggering multiple frames is set and not all image frames have been output yet.
Related commands :imgacq.
2.3 Video streaming mode
In video streaming mode, the camera continuously exposes and outputs images according to the configured ROI region and frame rate. It is recommended to get the maximum frame rate supported by the maxfps function after changing the ROI.
Related commands :trgmode,roi,fps,maxfps.
2.4 Normal trigger mode
2.4.1 Rolling shutter
For a rolling shutter sensor, such as IMX178, a complete image frame requires two image cycles to complete the process from exposure to output. So the maximum frame rate is half of the video streaming mode.
In normal trigger mode, for rolling shutter sensor, we refer to two consecutive frame cycles as one trigger cycle.
In normal trigger mode, if multiple frames are triggered at one time, the trigger delay acts after this trigger signal, and the trigger interval and exposure delay are valid before each trigger cycle.
2.4.2 Global shutter
TODO
2.5 High-speed continuous trigger mode
2.5.1 Rolling shutter
In high-speed trigger mode, assume Trigger Number is N, frames 2-N are output immediately after the previous frame and there is no more trigger interval. This allows the same maximum frame rate to be achieved as in video streaming mode.
3 Image Feature
4 ISP
5 IO Control