V4L2 mode for Raspberry Pi
How to use VEYE and CS series camera module on Raspberry Pi(V4L2 mode)
1 Introduction
For the use of VEYE series and CS series camera modules on the raspberry Pi platform, we provide veye_raspicam software, an application layer open source software similar to the raspicam. This series of software, without driver support, has good compatibility with different versions of piOS.
However, we think that the V4L2 driver mode also has a wide range of applications. The two modes cannot be used at the same time, which is embodied in whether the driver is installed or not. It will be described in detail later.
This article describes how to call the camera modules of VEYE series and CS series through V4L2 on the raspberry Pi platform.
2 Hardware Setup
VEYE series camera module setup on rpi
CS series camera module setup on rpi
3 RaspberryPi System Setup and Configuration
RaspberryPi System Setup and Configuration
4 Driver Installation
We have saved the code for v4l2 driver mode in this github repository.
4.1 Download the driver
wget https://github.com/veyeimaging/raspberrypi_v4l2/releases/latest/download/raspberrypi_v4l2.tgz
4.2 Install the driver
tar -xzvf raspberrypi_v4l2.tgz
cd raspberrypi_v4l2/release/
chmod +x *
sudo ./install_driver.sh [camera module]
camera module:could be veye327,csimx307,cssc132,veyecam2m.
Note: veyecam2m is a new version driver that can replace veye327 and supports all modules of the VEYE series with 200W resolution.
please use veyecam2m instead of veye327 which will be discarded.
Note: For VEYE-MIPI-IMX327S or VEYE-MIPI-IMX462, please make sure hdver must >= 0x5.
http://wiki.veye.cc/index.php/VEYE-MIPI-IMX327S_version_log
4.3 Uninstall the driver
If you need to change to using the camera by veye_raspicam software, or if you want to change to a driver of another camera module model, you must first uninstall the current driver.
sudo ./uninstall_driver.sh [camera module]
camera module:could be veye327,csimx307,cssc132,veyecam2m.
5 Check and Test the Camera
Check the camera probe status
- VEYE-MIPI-327
dmesg | grep veye
You can see:
veye327 camera probed
- CS-MIPI-IMX307
dmesg | grep 307
You can see:
camera id is cs-mipi-imx307
- CS-MIPI-SC132
dmesg | grep 132
You can see:
camera id is cs-mipi-sc132
5.1 List the video device
ls /dev/video0
The device node exsit.
5.2 List the available video modes
v4l2-ctl --list-formats-ext
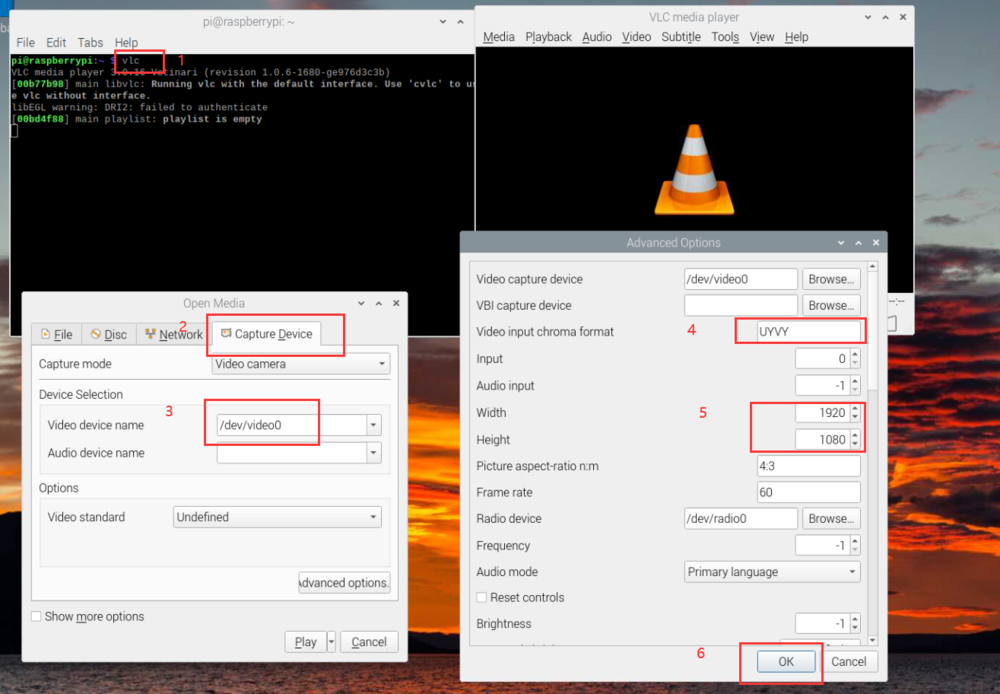
6 Preview using VLC
1. Open VLC with command line vlc , or click the icon to launch.
2. Hit the ▶(Play) button to call the open media window.
3. In Capture Device >> Device Selection >> Video device name, select the camera video node.
4. Hit Advanced Options... button
5. In Advanced Options window >> Video input chroma format, type UYUV.
6. Type in the width and height, for example, 1920 and 1080.
7. Hit OK to save the settings and see the video feed.
7 Gstreamer usage samples
export DISPLAY=:0
7.1 install gstreamer
sudo apt-get install gstreamer1.0-tools
sudo apt-get install libx264-dev libjpeg-dev
sudo apt-get install libgstreamer1.0-dev libgstreamer-plugins-base1.0-dev libgstreamer-plugins-bad1.0-dev gstreamer1.0-plugins-ugly gstreamer1.0-tools gstreamer1.0-gl gstreamer1.0-gtk3
7.2 Run gstreamer videotest command
gst-launch-1.0 videotestsrc ! videoconvert ! autovideosink
7.3 Snap a picture (VEYE-MIPI-327,CS-MIPI-IMX307 @1080p mode)
gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src num-buffers=1 device=/dev/video0 ! 'video/x-raw, format=(string)UYVY, width=1920,height=1080' ! jpegenc ! filesink location=test_image.jpg
7.4 Frame rate test (VEYE-MIPI-327,CS-MIPI-IMX307 @1080p mode)
gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=/dev/video0 ! "video/x-raw,format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1920, height=(int)1080,framerate=(fraction)30/1" ! videoconvert ! fpsdisplaysink video-sink=fakesink -v
7.5 Preview (VEYE-MIPI-327,CS-MIPI-IMX307 @1080p mode)
gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src io-mode=dmabuf device=/dev/video0 ! "video/x-raw,format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1920, height=(int)1080,framerate=(fraction)30/1" ! v4l2convert capture-io-mode=dmabuf output-io-mode=dmabuf ! autovideosink sync=false -v
7.6 Preview and Scale with timestamp on (VEYE-MIPI-327,CS-MIPI-IMX307 @1080p mode)
gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=/dev/video0 ! "video/x-raw,format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1920, height=(int)1080,framerate=(fraction)30/1" ! videoconvert ! videoscale ! clockoverlay time-format="%D %H:%M:%S" ! video/x-raw, width=640, height=360 ! autovideosink sync=false -v
7.7 Preview (CS-MIPI-IMX307,CS-MIPI-SC132 @720p mode)
gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=/dev/video0 ! "video/x-raw,format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1280, height=(int)720,framerate=(fraction)60/1" ! videoconvert ! autovideosink sync=false -v
7.8 Preview (CS-MIPI-IMX307,CS-MIPI-SC132 @vga mode)
gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=/dev/video0 ! "video/x-raw,format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)640, height=(int)480" ! videoconvert ! autovideosink sync=false -v
7.9 Preview (CS-MIPI-SC132 @1280*1080@45 mode)
gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=/dev/video0 ! "video/x-raw,format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1280, height=(int)1080,framerate=(fraction)45/1" ! videoconvert ! autovideosink sync=false -v
7.10 Streaming to file,save as mkv file(VEYE-MIPI-X,CS-MIPI-IMX307 @1080p mode)
gst-launch-1.0 -e v4l2src io-mode=dmabuf device=/dev/video0 num-buffers=300 ! "video/x-raw,format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1920, height=(int)1080,framerate=(fraction)30/1" ! v4l2h264enc capture-io-mode=dmabuf output-io-mode=dmabuf extra-controls="controls, h264_profile=4, video_bitrate=6200000" ! 'video/x-h264, profile=high, level=(string)4' ! h264parse ! matroskamux ! filesink location=output.mkv
7.11 Streaming to file,save as mp4 file(VEYE-MIPI-X,CS-MIPI-IMX307 @1080p mode)
gst-launch-1.0 -e v4l2src io-mode=dmabuf device=/dev/video0 num-buffers=300 ! "video/x-raw,format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1920, height=(int)1080,framerate=(fraction)30/1" ! v4l2h264enc capture-io-mode=dmabuf output-io-mode=dmabuf extra-controls="controls, h264_profile=4, video_bitrate=6200000" ! 'video/x-h264, profile=high, level=(string)4' ! h264parse ! mp4mux ! filesink location=video.mp4
7.12 TCP streaming
raspberrypi(sender)
gst-launch-1.0 -v v4l2src device=/dev/video0 num-buffers=-1 ! "video/x-raw,format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1920, height=(int)1080,framerate=(fraction)30/1" ! v4l2h264enc extra-controls="controls, h264_profile=4, video_bitrate=4000000" ! 'video/x-h264, profile=high, level=(string)4' ! h264parse ! rtph264pay config-interval=1 pt=96 ! gdppay ! tcpserversink host=x.x.x.x port=5000
The bandwidth of the stream is 4Mbps, continuous transmission, and the listening port is 5000.
Client
gst-launch-1.0 -v tcpclientsrc host=x.x.x.x port=5000 ! gdpdepay ! rtph264depay ! avdec_h264 ! autovideosink sync=false
Where x.x.x.x is the IP address of the Raspberry Pi (Server).
It is recommended to use powershell if client is a windows system. gstreamer windows version download here.
8 Stream to OpenCV
pip uninstall opencv-python
sudo apt install python3-opencv
To import camera data from v4l2 devices to opencv, we provide several samples.
9 V4l2-ctl usage examples
9.1 install v4l2-utils
sudo apt-get install v4l-utils
9.2 v4l2-ctl test
- Snap one UYVY raw data picture (1080p mode)
v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=1920,height=1080,pixelformat=UYVY --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=uyvy-1920x1080.yuv
- Snap 10 UYVY raw data pictures (1080p mode)
v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=1920,height=1080,pixelformat=UYVY --stream-mmap --stream-count=10 --stream-to=uyvy-1920x1080_stream.yuv
10 yavta usage examples
10.1 download yavta
git clone git://git.ideasonboard.org/yavta.git
cd yavta;make
10.2 yavta test
./yavta -c8 -Fuyvy_1920X1080.yuv --skip 0 -f UYVY -s 1920x1080 /dev/video0
PS, UYVY file can be played by YUV Displayer Deluxe.
11 Video Control Toolkits Manual
Because of the high flexibility of our camera parameters, we do not use V4L2 parameters to control, but use scripts to configure parameters.
https://github.com/veyeimaging/raspberrypi/tree/master/i2c_cmd
VEYE Series Video Control Toolkits Manual
CS Series Video Control Toolkits Manual
12 Notes for CM4
Cm4 supports the use of two cameras at the same time. Following above steps will only be able to use CAM1. To use two cameras, follow the following steps:
12.1 Upgrade dt-blob.bin
sudo wget https://datasheets.raspberrypi.com/cmio/dt-blob-dualcam.bin -O /boot/dt-blob.bin
12.2 Upgrade dual camera version dtbo file
Use csimx307 as an example:
sudo cp raspberrypi_v4l2/release/driver_bin/$(uname -r)/csimx307-dual-cm4.dtbo /boot/overlays/csimx307.dtbo
sudo reboot
12.3 Device node description
The CM4 module uses two I2C channels to communicate with the two cameras respectively.
| description | i2c bus num | video node |
|---|---|---|
| CAM0 | 0 | video0 |
| CAM1 | 10 | video2 |
Note: If there is only one camera, video node is always video0.
12.4 Gstreamer usage samples
export DISPLAY=:0
- CAM0 preview(VEYE-MIPI-327,CS-MIPI-IMX307 @1080p mode)
gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src io-mode=dmabuf device=/dev/video0 ! "video/x-raw,format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1920, height=(int)1080,framerate=(fraction)30/1" ! v4l2convert capture-io-mode=dmabuf output-io-mode=dmabuf ! autovideosink sync=false -v
- CAM1 preview(VEYE-MIPI-327,CS-MIPI-IMX307 @1080p mode)
gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src io-mode=dmabuf device=/dev/video2 ! "video/x-raw,format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1920, height=(int)1080,framerate=(fraction)30/1" ! v4l2convert capture-io-mode=dmabuf output-io-mode=dmabuf ! autovideosink sync=false -v
13 Source code compilation
Please refer to: Build drivers from source for rpi.
14 Document History
- 20220706
To optimize gstreamer's pipeline, it is recommended to use v4l2convert instead of videoconvert and try to use the capture-io-mode output-io-mode io-mode option.
- 20220505
Refine the description of CM4.
- 20220411
The source code compilation method is separate to a separate article.
- 20220302
Add v4l2-ctl and yavta examples.
- 20220301
Support 64-bit piOS
- 20220225
Add the application samples of gstreamer.
- 20211125
Add VLC preview section.