Difference between revisions of "VEYE CS Camera for Jetson TX2"
| Line 178: | Line 178: | ||
In gstreamer command ,v4l2src and nvv4l2camerasrc has a param device=/dev/videoX to identify which camera to use. | In gstreamer command ,v4l2src and nvv4l2camerasrc has a param device=/dev/videoX to identify which camera to use. | ||
=====Gstreamer Usage===== | =====Gstreamer Usage===== | ||
| + | To install the latest accelerated gstreamer plugins and applications, run the following commands: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>sudo apt-get update</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>sudo apt-get install nvidia-l4t-gstreamer</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>sudo ldconfig</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>rm -rf .cache/gstreamer-1.0/</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
<code>export DISPLAY=:0</code> | <code>export DISPLAY=:0</code> | ||
Revision as of 14:08, 12 August 2024
How to use VEYE and CS series camera module on NVIDIA Jetson Nano,TX2,Xavier and Orin
1 Overview
This guide shows how to use VEYE and CS series camera modules on Jetson boards. Jetson SDK Version is:
- Jetpack4.2.2,L4T r32.2.1
- Jetpack4.3,L4T r32.3.1
- Jetpack4.4,L4T r32.4.3
- Jetpack4.4.1,L4T r32.4.4
- Jetpack4.5,L4T r32.5
- Jetpack4.5.1,L4T r32.5.1
- Jetpack4.6,L4T r32.6.1
- Jetpack4.6.1, L4T r32.7.1
- Jetpack4.6.2,L4T r32.7.2
- Jetpack4.6.3,L4T r32.7.3
- Jetpack4.6.4,L4T r32.7.4
- Jetpack5.0.1DP, L4T r34.1.1
- Jetpack5.0.2, L4T r35.1
- Jetpack5.1,L4T r35.2.1
- Jetpack5.1.1,L4T r35.3.1
- Jetpack5.1.2,L4T r35.4.1
- Jetpack5.1.3,L4T r35.5
- Jetpack6.0,L4T r36.3
We provide two ways to do so: Prebuilt Binaries or Source Code. Yes, It's Open Source!
VEYE and CS series camera modules are camera module with ISP functions build in. It output UYVY data using MIPI-CSI2. We provide V4L2 interface for video streaming apps , and Video Control Toolkits (which is Shell Script) to control the camera module directly, which is called DRA(Directly Register Access).
1.1 Camera module list
| Series | Model | Status |
|---|---|---|
| VEYE series | VEYE-MIPI-IMX327S | Done |
| VEYE series | VEYE-MIPI-IMX385 | Done |
| VEYE series | VEYE-MIPI-IMX462 | Done |
| VEYE series | VEYE-MIPI-IMX335 | Done |
| CS series | CS-MIPI-IMX307 | Done |
| CS series | CS-MIPI-SC132 | Done |
| TX2-XAVIER-nCAM Series | CS-TX2-XAVIER-nCAM | Done |
1.2 How to check the current L4T version
1.2.1 Method 1
On Jetson board
cat /etc/nv_tegra_release
If it shows:
# R32 (release), REVISION: 4.3......
It means L4t Version is 32.4.3
1.2.2 Method 2
Refer to this link to install jetson-stats:
jtop
2 Hardware Setup
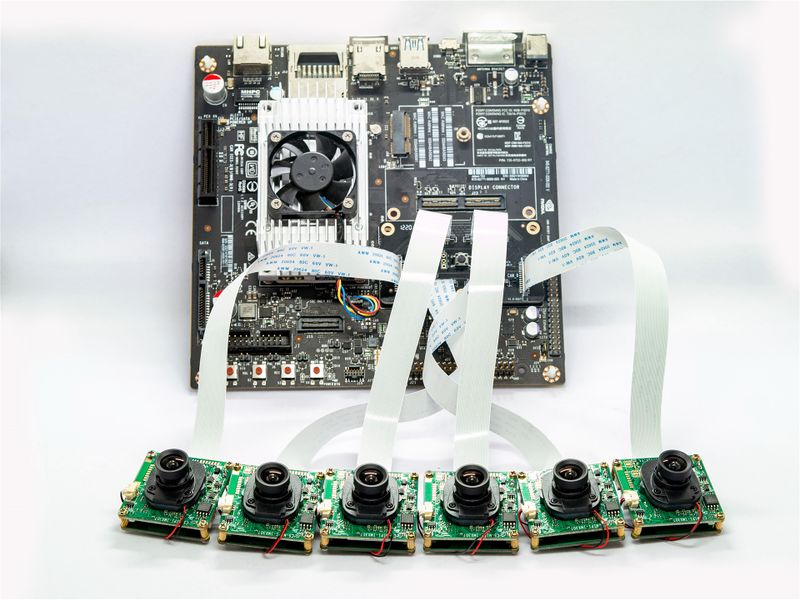
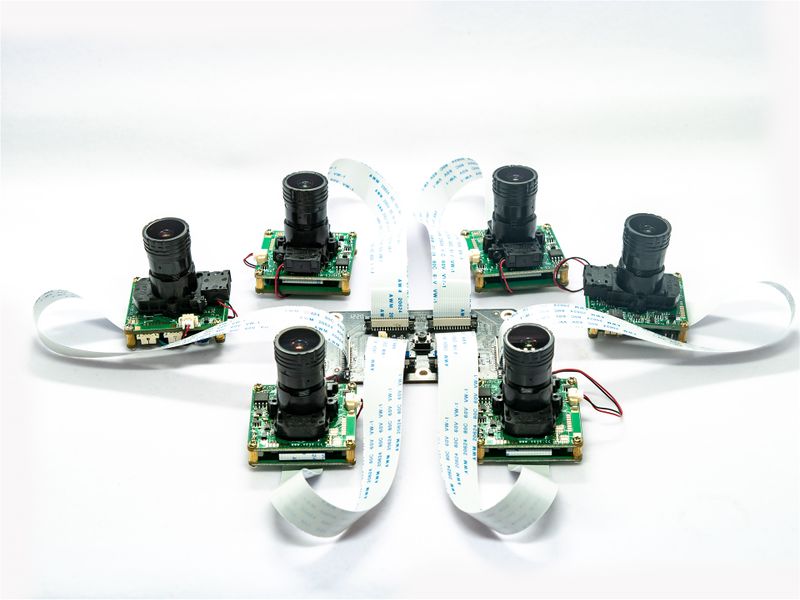
We have designed a 6cam interposer board for TX2 devkit,Xavier and Orin, It support up to 6 cameras at the same time.
In particular, the VEYE-MIPI-IMX335 must use a 12V DC terminal to provide auxiliary power due to its high power consumption. Refer to J11 of ADP-N1.
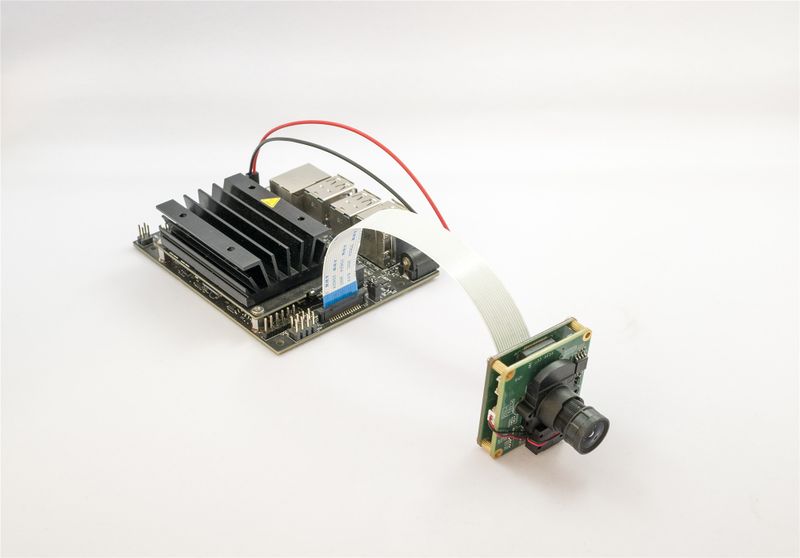
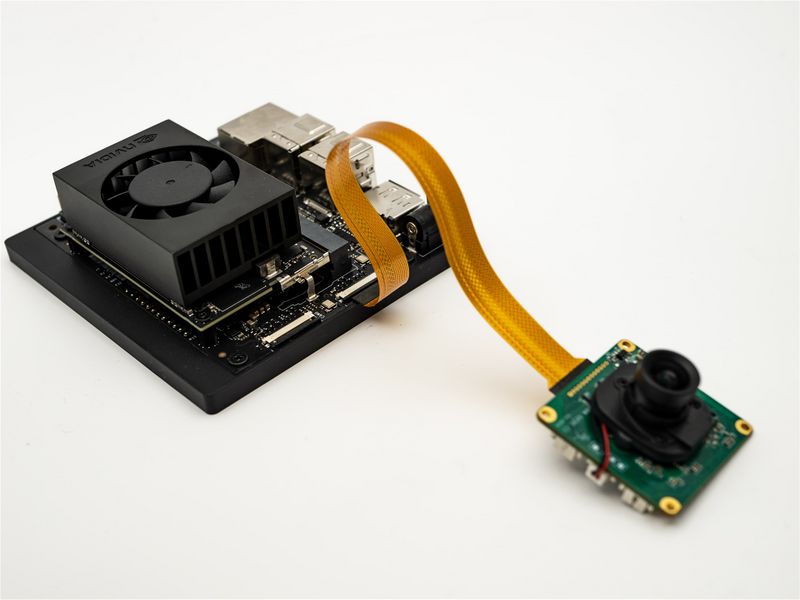
2.1 NVIDIA TX2 Developer Kit
It is connected as shown in figure:
Be sure to screw the ADP adapter board to the bottom board.
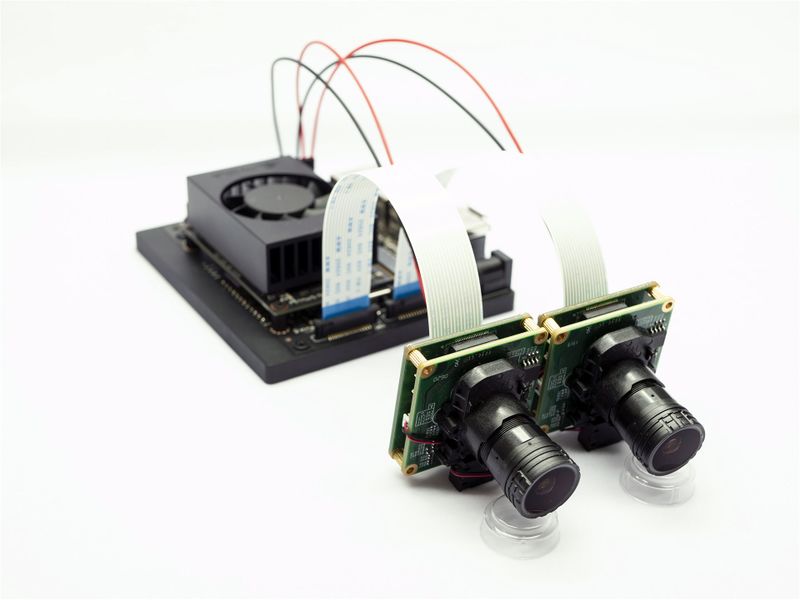
2.2 NVIDIA AGX Xavier(the same with Orin)
Be sure to screw the ADP adapter board to the bottom board to ensure that the adapter plate is installed flat.
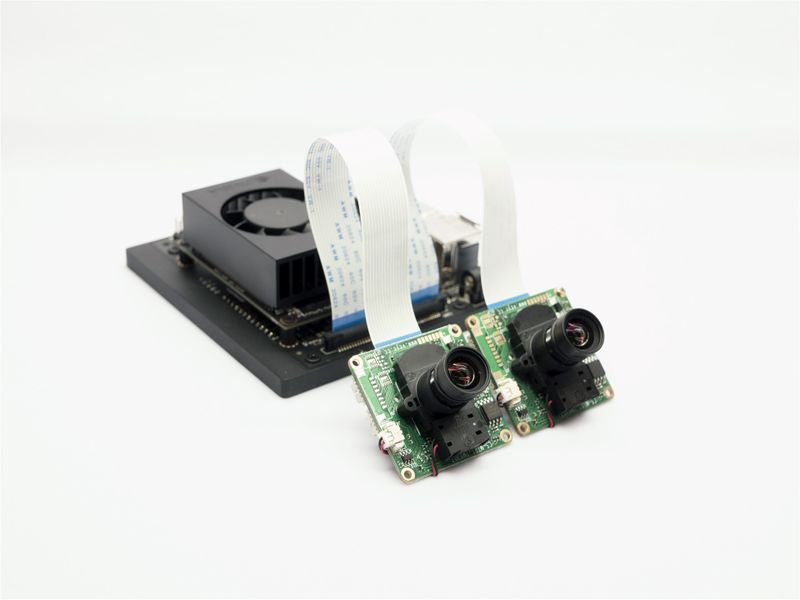
2.3 NVIDIA Nano ,TX2 NX and Xavier NX Devkit
The Xavier NX interface is compatible with raspberry pi and Jetson Nano. The connection mode is shown in figure:
3 Upgrade Jetson system
This section describes how to upgrade the Jetson system to support MV camera module. For OS update method, please refer to Update Jetson OS.
4 Applications and Test
4.1 Check system status
Run the following command to confirm whether the camera is probed.
- VEYE-MIPI-IMX327S/VEYE-MIPI-IMX462/VEYE-MIPI-IMX385(using VEYE-MIPI-CAM2M dtb)
dmesg | grep veye
The output message appears as shown below:
camera id is veyecam
sensor is IMX327/IMX462/IMX385
subdev veyecam [i2c_bus]-003b bound
- For CS-MIPI-IMX307
dmesg | grep csx307
The output message appears as shown below.:
Detected CS307 sensor
subdev csx307 [i2c_bus]-003b bound
- For CS-MIPI-SC132
dmesg | grep cssc132
The output message appears as shown below.:
subdev cssc132 [i2c_bus]-003b bound
- For VEYE-MIPI-IMX335
dmesg | grep imx335
The output message appears as shown below.:
camera id is VEYE-MIPI-IMX335
subdev veye_imx335 [i2c_bus]-003b bound
- Run the following command to check the presence of video node.
ls /dev/video*
The output message appears as shown below.
videoX
- For VEYE-MIPI-327(using VEYE-MIPI-327 dtb)
dmesg | grep veye327
The output message appears as shown below:
Detected VEYE327 sensor
subdev veye327 [i2c_bus]-003b bound
The [i2c_bus] in the driver prompt message indicates the i2c bus corresponding to this camera.
4.2 Video Stream Toolkits Manual
The camera appears as /dev/videoX device node,where X is between [0-5].
During the Linux boot process, the cameras are detected in the order of i2c bus from smallest to largest. For example, if only one camera is connected, X is 0 regardless of the hardware connection to the location. If 5 cameras are connected, X is reflected as [0-4] according to i2c bus from smallest to largest.
In gstreamer command ,v4l2src and nvv4l2camerasrc has a param device=/dev/videoX to identify which camera to use.
4.2.1 Gstreamer Usage
To install the latest accelerated gstreamer plugins and applications, run the following commands:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install nvidia-l4t-gstreamer
sudo ldconfig
rm -rf .cache/gstreamer-1.0/
export DISPLAY=:0
- Preview FHD
gst-launch-1.0 nvv4l2camerasrc device=/dev/video0 ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1920, height=(int)1080" ! nvvidconv ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)I420" ! nv3dsink sync=false
gst-launch-1.0 nvv4l2camerasrc device=/dev/video0 ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1920, height=(int)1080" ! nvvidconv ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)NV12" ! nv3dsink sync=false
- Preview FHD(using xvimagesink sink if supported)
export DISPLAY=:0
gst-launch-1.0 -e v4l2src io-mode=4 device=/dev/video0 do-timestamp=true ! 'video/x-raw, width=1920, height=1080, framerate=30/1, format=UYVY' ! xvimagesink sync=false
- Preview 720p@60 (CS-MIPI-IMX307)
gst-launch-1.0 nvv4l2camerasrc ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1280, height=(int)720, framerate=(fraction)60/1" ! nvvidconv ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)I420" ! nv3dsink sync=false
- Preview 1280*1080@45 (CS-MIPI-SC132)
gst-launch-1.0 nvv4l2camerasrc ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1280, height=(int)1080, framerate=(fraction)45/1" ! nvvidconv ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)I420" ! nv3dsink sync=false
- Preview 640*480p@130 (CS-MIPI-IMX307)
gst-launch-1.0 nvv4l2camerasrc ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)640, height=(int)480, framerate=(fraction)130/1" ! nvvidconv ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)I420" ! nv3dsink sync=false
- Preview 2 cameras 1080p HD
WIDTH=960
HEIGHT=540
CAPS="video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)UYVY, width=1920, height=1080"
gst-launch-1.0 nvcompositor name=comp sink_0::xpos=0 sink_0::ypos=0 sink_0::width=$WIDTH sink_0::height=$HEIGHT sink_1::xpos=$WIDTH sink_1::ypos=0 sink_1::width=$WIDTH sink_1::height=$HEIGHT ! nv3dsink nvv4l2camerasrc device=/dev/video0 ! $CAPS ! nvvidconv ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)I420"! comp. nvv4l2camerasrc device=/dev/video1 ! $CAPS ! nvvidconv ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)I420"! comp.
- Record FHD in H.264 format to a video file
gst-launch-1.0 nvv4l2camerasrc num-buffers=300 ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1920, height=(int)1080" ! nvvidconv ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)NV12" ! nvv4l2h264enc control-rate=1 bitrate=10000000 ! h264parse ! qtmux ! filesink location=filename.mp4 -e
- Playback of saved video file
gst-launch-1.0 filesrc location=filename.mp4 ! qtdemux ! queue ! h264parse ! nvv4l2decoder ! nvoverlaysink -e
- Capturing FHD still image
gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src num-buffers=1 ! "video/x-raw,format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1920, height=(int)1080" ! nvvidconv ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)I420" ! nvjpegenc ! filesink location=jpgname.jp
4.2.2 VEYE-MIPI-IMX335 gstreamer example
Since VEYE-MIPI-IMX335 supports only a few specific resolution modes, its driver we use use_sensor_mode_id mode.
| ./veye5_mipi_i2c.sh video mode | v4l2-ctl sensor_mode | video format |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 2592x1944@20fps |
| 2 | 1 | 2592x1944@12.5fps |
| 3 | 2 | 2560x1440@25fps |
| 4 | 3 | 2560x1440@30fps |
- prepare
sudo apt-get install v4l-utils
Refer to the following section and download the veye5_mipi_i2c.sh tool.
- 2592x1944@20fps mode preview, framerate statistics
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-ctrl sensor_mode=0
./veye5_mipi_i2c.sh -w -f videomode -p1 1 -b [busnum]
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-ctrl preferred_stride=5376
Preview
gst-launch-1.0 nvv4l2camerasrc device=/dev/video0 ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM), width=(int)2592, height=(int)1944" ! nvvidconv ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)I420" ! nv3dsink sync=false
Framerate statistics
gst-launch-1.0 nvv4l2camerasrc device=/dev/video0 ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)UYVY,width=(int)2592,height=(int)1944" ! nvvidconv ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)I420" ! fpsdisplaysink video-sink=fakesink -v
- 2560x1440@30fps mode video encode and capture
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-ctrl sensor_mode=3
./veye5_mipi_i2c.sh -w -f videomode -p1 4 -b [busnum]
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-ctrl preferred_stride=5120
Video encode
gst-launch-1.0 nvv4l2camerasrc num-buffers=300 ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)2560, height=(int)1440" ! nvvidconv ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)NV12" ! nvv4l2h264enc control-rate=0 bitrate=10000000 ! h264parse ! qtmux ! filesink location=filename.mp4 -e
Video Replay
gst-launch-1.0 filesrc location=filename.mp4 ! qtdemux ! queue ! h264parse ! nvv4l2decoder ! nv3dsink -e
Capture
gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src num-buffers=1 ! "video/x-raw,format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)2560, height=(int)1440" ! nvvidconv ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)I420" ! nvjpegenc ! filesink location=jpgname.jpg
4.2.3 Jetson multimedia-api samples
The Jetson Linux API is available on the Jetson platform for developers to use. Please refer to the official nVidia documentation for the installation of the jetson_multimedia_api package.
For VEYE and CS series cameras, the ISP function is already integrated in the camera, so you cannot use libargus to get data, but can directly use the standard V4L2 interface to get data from the /dev/videoX device file.
The following two samples can be run directly.
4.2.3.1 12_camera_v4l2_cuda
./camera_v4l2_cuda -d /dev/video0 -s 1920x1080 -f UYVY
4.2.3.2 v4l2cuda
./capture-cuda -d /dev/video0 -f UYVY -m -o out.ppm -s 1920x1080 -c 1
4.2.4 v4l2-ctl Application Examples
4.2.4.1 install v4l2-utils
sudo apt-get install v4l-utils
4.2.4.2 Configure parameters using v4l2-ctl
- List the data formats supported by the camera
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --list-formats-ext
- Frame rate statistics
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=1920,height=1080,pixelformat=UYVY--stream-mmap --stream-count=-1 --stream-to=/dev/null
- Save image to file
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=1920,height=1080,pixelformat=UYVY --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=uyvy-1920x1080.yuv
4.2.5 yavta
4.2.5.1 install yavta
git clone https://github.com/veyeimaging/yavta.git
cd yavta;make
4.2.5.2 Save image to file
./yavta -c1 -FUYVY-1920x1080.yuv --skip 0 -f UYVY -s 1920x1080 /dev/video0
4.2.6 Opencv
To import camera data from v4l2 devices to opencv, we provide several samples.
We provide 2 samples here.
4.3 Using i2c script to modify camera parameters
- VEYE-MIPI-CAM2M Series(VEYE-MIPI-327、VEYE-MIPI-IMX327S、VEYE-MIPI-IMX462、VEYE-MIPI-IMX385)
Video Control Toolkits Manual :VEYE-MIPI-327 I2C
- CS-MIPI-IMX307和CS-MIPI-SC132
Video Control Toolkits Manual :CS-MIPI-X I2C
- VEYE-MIPI-IMX335
Video Control Toolkits Manual :VEYE-MIPI-IMX335 I2C
5 How to port the driver to a third party board
5.1 driver porting
For Image, we have added functionality to the official standard Image and have not made any deletions. In general, you can use our compiled Image directly. for special cases, please refer to the source code for integration.
For modules it is even easier to just use them. Compiling from source code and is very simple, so I won't go into details here.
5.2 dts porting
We only provide dtb for some boards of Nano, TX2, Xavier, Orin. For the types not provided, it is necessary to:
1. get the dts source code of that board.
2. put our camera related dts to the whole.
3. recompile to get the dtb of the corresponding board.
The operation steps are not complicated, but there are some third-party base board manufacturers do not open dts source code. This will require the cooperation of all parties to do so.
6 FAQ and bug list
6.1 Problem of system update not taking effect on a system with an SSD hard drive
If an SSD hard drive is installed in a system and mounted on the / directory, it may cause regular system update operations (Image, ko, dtb) to be completely ineffective.
The reason for this is that the board comes with an eMMC storage device, and the Image, ko, and dtb that take effect during the boot stage are stored in the eMMC.
After the boot is completed, if the SSD hard drive is mounted on the / directory, it may cause the files stored on the eMMC to be inaccessible.
The solution in this case is to manually mount the mmcblk0p1 partition of the eMMC to a specific directory, and perform all system update operations based on this directory.
6.2 VEYE cameras on Jetpack5.x
Jetpack5.x has more stringent requirements for mipi signals in xavier and orin platforms. VEYE-MIPI-xxx series cameras need firmware hdver>=7 to be perfectly supported.
6.3 CS-MIPI-IMX307 combined with Orin nano and Orin NX Green Screen
When CS-MIPI-IMX307 is powered by the 3.3V mode of the FFC cable, the MIPI receiver state machine of Orin nano and Orin NX (Jetpack5.1.1) will enter an incorrect state.
It is recommended to refer to this article and modify the power supply mode of CS-MIPI-IMX307 to use the 5V power supply mode.
6.4 Jetpack5.0.1 DP
This version has many bugs, such as not supporting nvv4l2camerasrc, not recommended to use.
6.5 nv3dsink
Jetpack 5.x no longer supports nvoverlaysink, use nv3dsink instead.
6.6 cboot of L4T32.7.2 on Xavier
For the Xavier series, there is a bug in the cboot of L4T32.7.2 that must be fixed before the upgrade can be done.
[Cboot] Cboot in 32.7.2 fails to read extlinux.conf
We compiled the correct version of cboot and put it here.
After downloading, put it in Linux_for_Tegra/bootloader directory and execute the following command on PC to burn cboot.
- AGX Xavier
sudo ./flash.sh -r -k cpu-bootloader jetson-xavier mmcblk0p1
- Xavier NX
sudo ./flash.sh -r -k cpu-bootloader jetson-xavier-nx-devkit mmcblk0p1
7 Document History
- 2024-08-06
Make Chapter 3 - Upgrading the Jetson system a separate article.
- 2024-05-22
Add support for Jetpack5.1.3.
- 20230427
Add support for Jetpack5.1.1.
- 20230222
Add support for Jetpack5.1.
- 20220831
Improve the description of VEYE series and MV series under Jetpack 5.0.2.
- 20220824
Add support for Jetpack5.0.2.
- 20220720
Add multimedia-api samples and v4l2 samples.
- 20220714
Add L4T32.7.2 Note。
- 20220629
Add support for Jetpack 5.0.1DP and tune through AGX-Orin.
- 20220110
Add VEYE-MIPI-IMX385 support.
- 20220105
Use nvv4l2h264enc instead of omxh264enc in gstreamer command,because omxh264enc has been deprecated.
- 20211025
Use nvcamerasrc instead of v4l2src in gstreamer command , and the data goes directly into DMA memory.
8 References
Jetson start up: https://developer.nvidia.com/embedded/learn/getting-started-jetson
Jetson Download Center: https://developer.nvidia.com/embedded/downloads
Xavier NX: https://developer.nvidia.com/embedded/learn/get-started-jetson-xavier-nx-devkit
TX2 development kit: https://developer.nvidia.com/embedded/jetson-tx2-developer-kit
SDK Manager: https://docs.nvidia.com/sdk-manager/index.html
L4T Doc: https://docs.nvidia.com/jetson/archives/l4t-archived/l4t-3242/index.htm
TX2 user guide: link