Difference between revisions of "Mv series camera appnotes 4 rpi"
| (46 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
|MV series | |MV series | ||
|MV-MIPI-IMX296M | |MV-MIPI-IMX296M | ||
| + | |Done | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |MV series | ||
| + | |MV-MIPI-IMX287M | ||
|Done | |Done | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 36: | Line 40: | ||
|RAW series | |RAW series | ||
|RAW-MIPI-SC132M | |RAW-MIPI-SC132M | ||
| + | |Done | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |RAW series | ||
| + | |RAW-MIPI-IMX462M | ||
| + | |Done | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |RAW series | ||
| + | |RAW-MIPI-AR0234M | ||
|Done | |Done | ||
|} | |} | ||
=== Hardware Setup === | === Hardware Setup === | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== MV series cameras use the ADP-MV1 connection ==== | ||
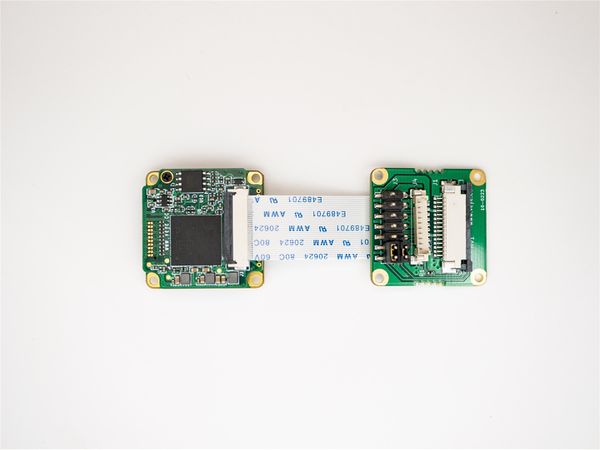
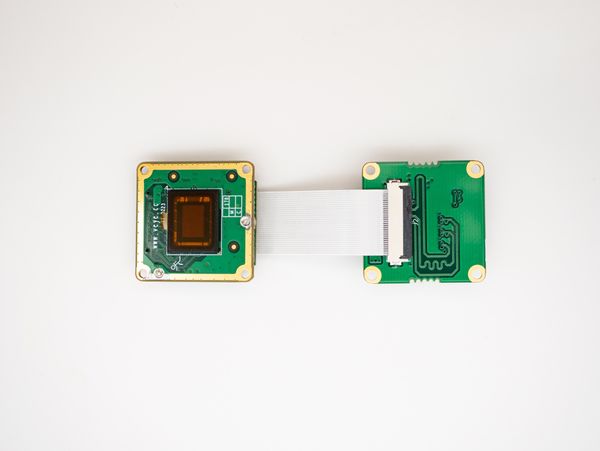
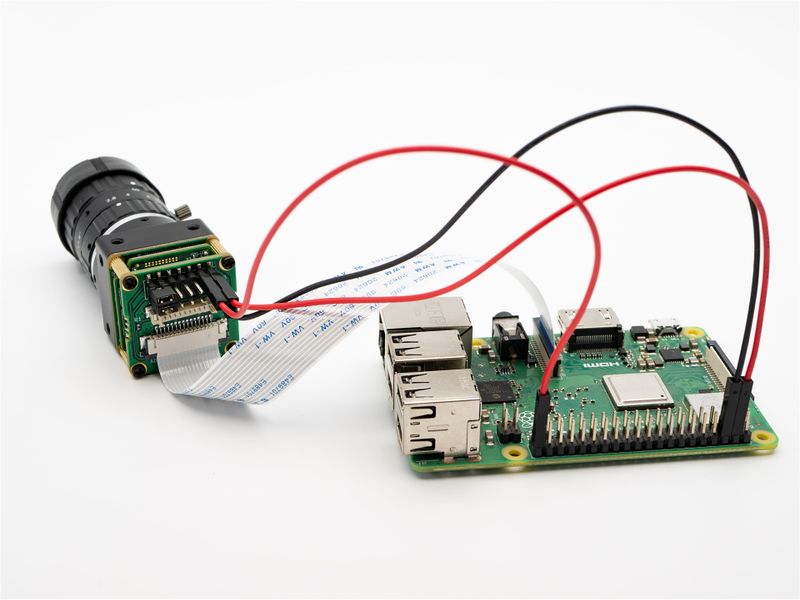
MV series cameras need to use ADP-MV1 adapter board in order to connect to Raspberry Pi. | MV series cameras need to use ADP-MV1 adapter board in order to connect to Raspberry Pi. | ||
| − | + | ===== Connection of MV series camera and ADP-MV1 ===== | |
| − | + | The two are connected using 0.5 mm pitch*30P FFC cable with opposite-side contacts. The cable must be inserted with the silver contacts facing outside. | |
| − | ==== Connection of MV | ||
| − | The two are connected using 0.5 mm pitch*30P FFC cable with opposite | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
!TOP | !TOP | ||
| Line 54: | Line 66: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | ==== | + | ===== Power supply ===== |
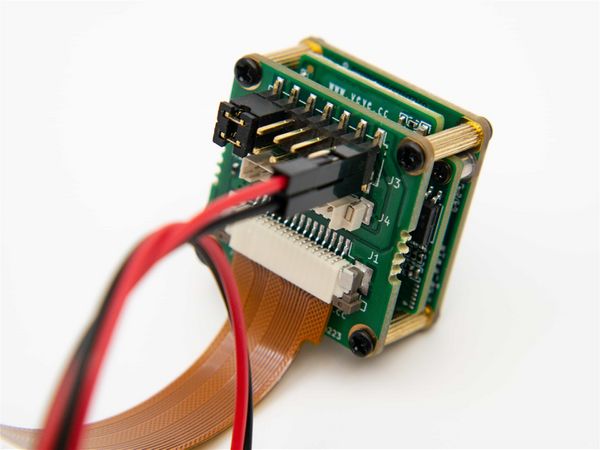
| − | |||
The ADP-MV1 requires a separate 5V power supply and can be powered directly from the Raspberry Pi motherboard using a Dupont cable.[[File:ADP-MV1-MV-MIPI-X 07.jpg|center|thumb|800x800px|ADP-MV1 power supply|link=http://wiki.veye.cc/index.php/File:ADP-MV1-MV-MIPI-X_07.jpg]] | The ADP-MV1 requires a separate 5V power supply and can be powered directly from the Raspberry Pi motherboard using a Dupont cable.[[File:ADP-MV1-MV-MIPI-X 07.jpg|center|thumb|800x800px|ADP-MV1 power supply|link=http://wiki.veye.cc/index.php/File:ADP-MV1-MV-MIPI-X_07.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Raspberry Pi 5 ===== | ||
| + | The two are connected using 15Pto22P FFC cable with Same-side contacts. Pay attention to the silver contacts facing side. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:ADP-MV1 to RPI5.jpg|link=http://wiki.veye.cc/index.php/File:ADP-MV1%20to%20RPI5.jpg|center|thumb|600x600px|ADP-MV1 to RPI5]] | ||
| + | |[[File:ADP-MV1 to RPI5 2.jpg|link=http://wiki.veye.cc/index.php/File:ADP-MV1%20to%20RPI5%202.jpg|alt=|center|thumb|600x600px|ADP-MV1 to RPI5_2]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
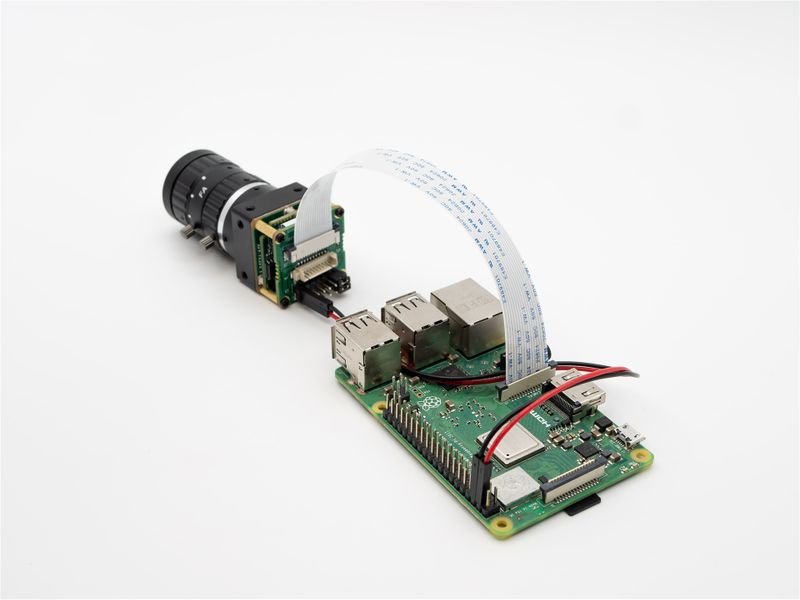
===== Raspberry Pi Model B and B+ ===== | ===== Raspberry Pi Model B and B+ ===== | ||
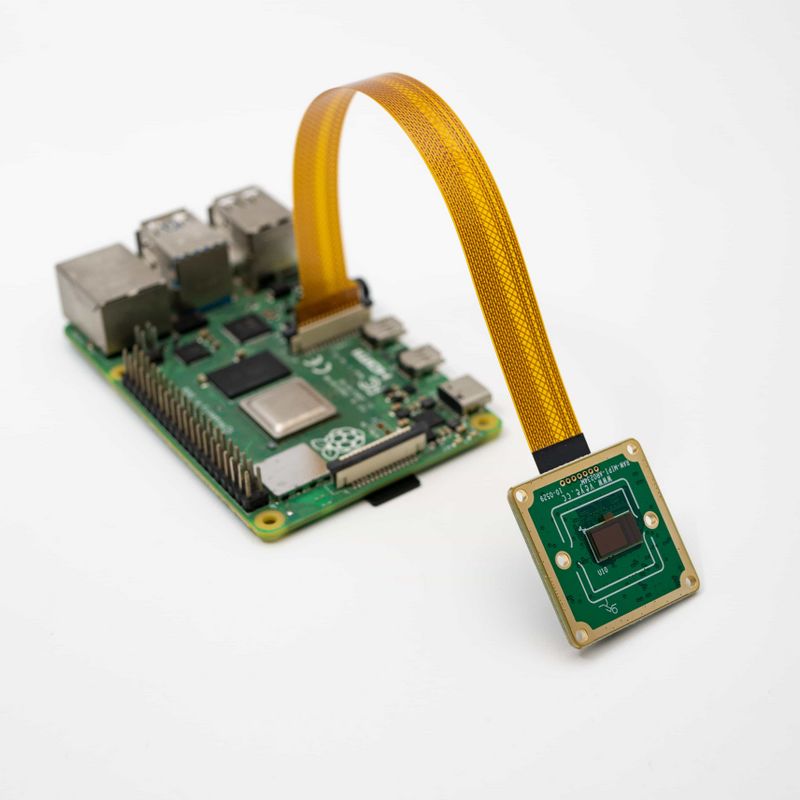
| − | The two are connected using 1.0 mm pitch*15P FFC cable with opposite | + | The two are connected using 1.0 mm pitch*15P FFC cable with opposite-side contacts. Pay attention to the silver contacts facing side.[[File:MV-MIPI-X-RPI B 01.jpg|alt=MV camera and RPI connection|center|thumb|800x800px|MV camera and RPI connection|link=http://wiki.veye.cc/index.php/File:MV-MIPI-X-RPI_B_01.jpg]] |
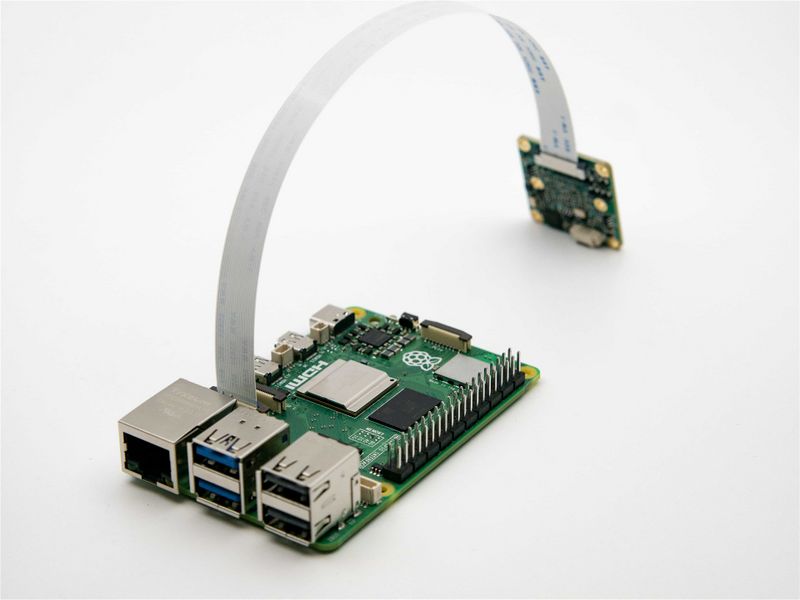
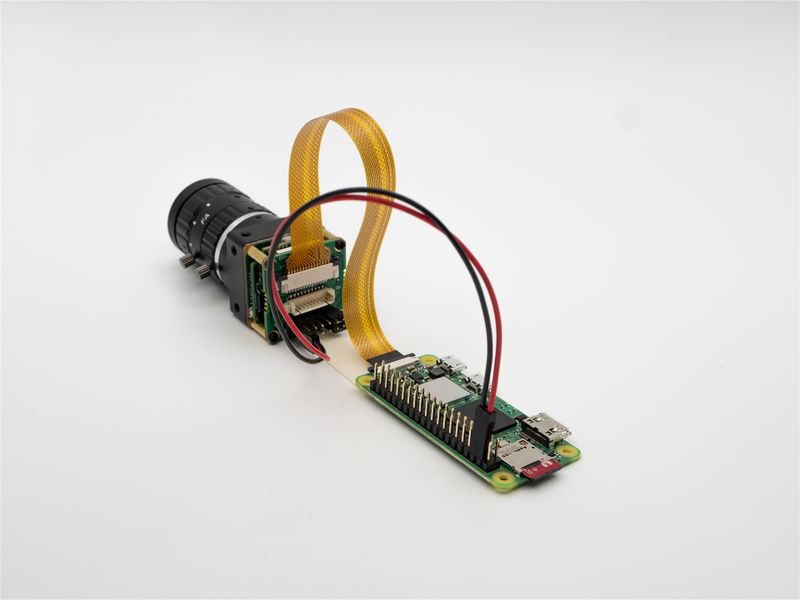
===== Raspberry Pi Zero, Zero W and Computer Module ===== | ===== Raspberry Pi Zero, Zero W and Computer Module ===== | ||
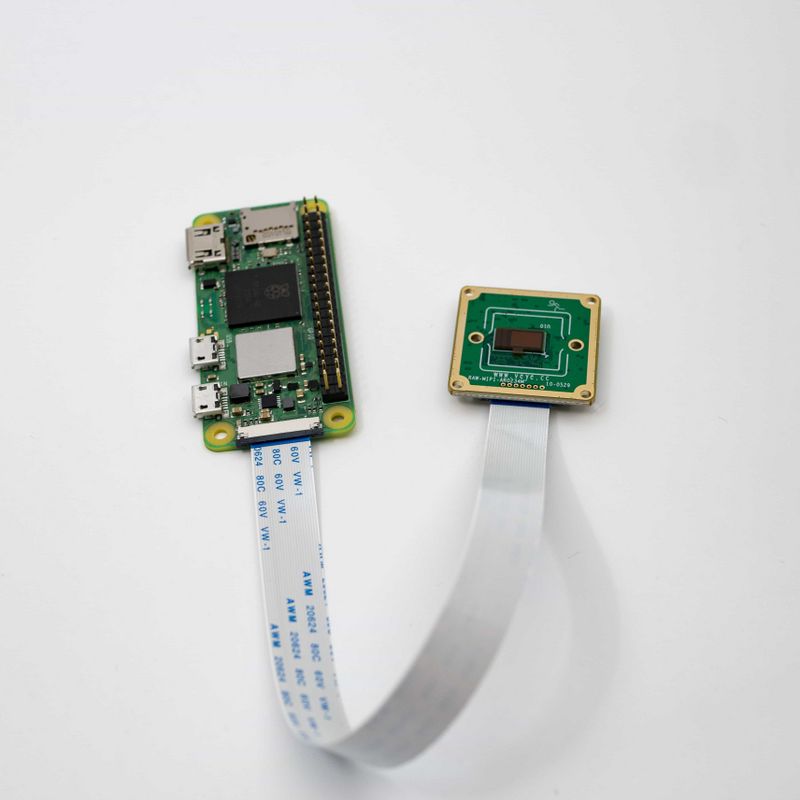
| − | The two are connected using 15Pto22P FFC cable with | + | The two are connected using 15Pto22P FFC cable with Same-side contacts. Pay attention to the silver contacts facing side.[[File:MV-MIPI-X-RPI Z 01.jpg|center|thumb|800x800px|MV camera and Raspberry Pi zero connection|link=http://wiki.veye.cc/index.php/File:MV-MIPI-X-RPI_Z_01.jpg]]<br /> |
| + | ====RAW series cameras directly connected to Raspberrypi==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Raspberry Pi 5 ===== | ||
| + | The RAW-MIPI-SC132M use a 15-to-22-pin same-side FFC cable, while other RAW series cameras use a 22-pin opposite-side FFC cable. | ||
| + | [[File:RAW CAM to RPI5.jpg|link=http://wiki.veye.cc/index.php/File:RAW%20CAM%20to%20RPI5.jpg|center|thumb|800x800px|RAW CAM to RPI5]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | =====Raspberry Pi Model B and B+===== | ||
| + | The RAW-MIPI-SC132M use a 15-pin opposite-side FFC cable, while other RAW series cameras use a 15-to-22-pin same-side FFC cable.[[File:RAW-MIPI-AR0234-RPI4.jpg|center|thumb|800x800px|RAW series camera and RPI connection|link=http://wiki.veye.cc/index.php/File:RAW-MIPI-AR0234-RPI4.jpg]] | ||
| + | =====Raspberry Pi Zero, Zero W and Computer Module===== | ||
| + | The RAW-MIPI-SC132M use a 15-to-22-pin same-side FFC cable, while other RAW series cameras use a 22-pin opposite-side FFC cable.[[File:RAW-MIPI-AR0234-RPI ZERO.jpg|center|thumb|800x800px|RAW-MIPI-AR0234-RPI ZERO|link=http://wiki.veye.cc/index.php/File:RAW-MIPI-AR0234-RPI_ZERO.jpg]] | ||
=== piOS Configuration === | === piOS Configuration === | ||
For details on how to install the Raspberry Pi system, please refer to the official documentation at [https://www.raspberrypi.org/documentation/installation/ Install raspberry pi guide]. | For details on how to install the Raspberry Pi system, please refer to the official documentation at [https://www.raspberrypi.org/documentation/installation/ Install raspberry pi guide]. | ||
| Line 71: | Line 100: | ||
It is recommended to enable the ssh service and samba service of Raspberry Pi system, here we will not go into the details of how to enable ssh and samba service of Raspberry Pi system. | It is recommended to enable the ssh service and samba service of Raspberry Pi system, here we will not go into the details of how to enable ssh and samba service of Raspberry Pi system. | ||
| − | === | + | === V4L2 mode and Legacy mode introduction === |
| − | + | In the latest Raspberry Pi Bookworm system, support for Legacy mode has been removed. It is recommended for customers to use the V4L2 mode. | |
| + | |||
| + | ==== libcamera and V4L2 mode ==== | ||
| + | Now piOS has switched to libcamera-stack mode. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Libcamera is essentially centered on implementing isp functionality, something that is not needed for the MV series cameras. Therefore, we have adopted the V4L2 mode instead of using libcamera-stack. | ||
| + | As with libcamera-stack, our V4L2 model implements the standard V4L2 driver for the linux driver layer too. Based on this driver, the application layer can directly develop programs to acquire images and perform further processing. | ||
==== Legacy mode ==== | ==== Legacy mode ==== | ||
Traditional mode, relying on Broadcom's GPU for image processing. The traditional raspicam software set uses this model. | Traditional mode, relying on Broadcom's GPU for image processing. The traditional raspicam software set uses this model. | ||
| Line 91: | Line 126: | ||
Since the two modes cannot co-exist, Legacy mode needs to be turned off when using V4L2 mode. | Since the two modes cannot co-exist, Legacy mode needs to be turned off when using V4L2 mode. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Configuring global variables=== | ===Configuring global variables=== | ||
For the convenience of later descriptions, global variables are configured here according to the sensor size. | For the convenience of later descriptions, global variables are configured here according to the sensor size. | ||
| Line 124: | Line 152: | ||
<code>export FPS=60</code> | <code>export FPS=60</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *MV-MIPI-IMX287M | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>export WIDTH=704</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>export HEIGHT=544</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>export FPS=319</code> | ||
*MV-MIPI-IMX265M | *MV-MIPI-IMX265M | ||
| Line 139: | Line 175: | ||
<code>export HEIGHT=2056</code> | <code>export HEIGHT=2056</code> | ||
| − | <code>export FPS= | + | <code>export FPS=28</code> |
*RAW-MIPI-SC132M | *RAW-MIPI-SC132M | ||
| − | <code>export WIDTH= | + | <code>export WIDTH=1024</code> |
<code>export HEIGHT=1280</code> | <code>export HEIGHT=1280</code> | ||
<code>export FPS=120</code> | <code>export FPS=120</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *RAW-MIPI-IMX462M | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>export WIDTH=1920</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>export HEIGHT=1088</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * <code>export FPS=60</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *RAW-MIPI-AR0234M | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>export WIDTH=1920</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>export HEIGHT=1200</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>export FPS=60</code> | ||
===V4L2 mode manual=== | ===V4L2 mode manual=== | ||
We have saved the code for v4l2 mode in this [https://github.com/veyeimaging/raspberrypi_v4l2 github repository]. | We have saved the code for v4l2 mode in this [https://github.com/veyeimaging/raspberrypi_v4l2 github repository]. | ||
| Line 158: | Line 210: | ||
<code>chmod +x *</code> | <code>chmod +x *</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * For Raspberry Pi 5 | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>sudo ./install_driver_rpi5.sh veye_mvcam</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | It will install both CAM1 and CAM0 overlays in /boot/config.txt. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * For other Raspberry Pi | ||
<code>sudo ./install_driver.sh veye_mvcam</code> | <code>sudo ./install_driver.sh veye_mvcam</code> | ||
| Line 182: | Line 242: | ||
And the /dev/video0 node exists, which proves that the camera status is normal. | And the /dev/video0 node exists, which proves that the camera status is normal. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Raspberry Pi 5 Setting ==== | ||
| + | On Raspberry Pi 5,the drivers now use the media controller API, and we must setup the media graph correctly first. This includes setting up the media pad formats correctly and correctly linking them together. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We provide a series of scripts to implement this functionality, saved in the rpi5_scripts directory. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * ./find_entity.sh | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>$ ./find_entity.sh</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>Found mvcam @ i2c-4 entity on /dev/media3</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>Plese get frame from /dev/video0 and use /dev/v4l-subdev2 for camera setting.</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>Found mvcam @ i2c-6 entity on /dev/media0</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>Plese get frame from /dev/video8 and use /dev/v4l-subdev5 for camera setting.</code><br />After a reboot of Raspberry Pi 5, the media node and video node of the camera may change. Therefore, it is recommended to execute <code>./find_entity.sh</code> before performing subsequent operations to identify the device nodes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The above prompt shows that the system has detected two cameras and their corresponding device nodes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>i2c-4</code> corresponds to the CAM1 port on the board, and <code>i2c-6</code> corresponds to the CAM0 port on the board. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * media_setting_rpi5.sh | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>./media_setting_rpi5.sh</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>Usage: ./media_setting_rpi5.sh veyecam2m/csimx307/cssc132/mvcam -fmt [UYVY/RAW8/RAW10/RAW12] -w [width] -h [height]</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>This shell script is designed to detect the connection of a camera on Raspberry Pi 5.</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code> It utilizes media-ctl and v4l2-ctl commands to configure the linking relationships and data formats of the media pad.</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code> Once completed, you can directly use /dev/video0 or /dev/video8 to obtain image data</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Before proceeding with further operations, it is '''necessary''' to execute this script to complete the configuration of parameters. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For instance,RAW-MIPI-AR0234M: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>./media_setting_rpi5.sh mvcam -fmt RAW8 -w 1920 -h 1200</code> | ||
==== v4l2-ctl application examples ==== | ==== v4l2-ctl application examples ==== | ||
| Line 221: | Line 320: | ||
<small><code> Size: Discrete 3088x2064</code></small> | <small><code> Size: Discrete 3088x2064</code></small> | ||
| − | < | + | <br />On Raspberry Pi 5, the actual supported image formats depend on the capabilities of the camera, not the list provided here. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
====== List the configurable parameters of the camera implemented in the driver ====== | ====== List the configurable parameters of the camera implemented in the driver ====== | ||
<code>v4l2-ctl -L</code> | <code>v4l2-ctl -L</code> | ||
| − | <code | + | <code>User Controls</code> |
| − | <code | + | <code> trigger_mode 0x00981901 (int) : min=0 max=2 step=1 default=0 value=0 flags=volatile, execute-on-write</code> |
| − | <code | + | <code> trigger_src 0x00981902 (int) : min=0 max=1 step=1 default=1 value=1 flags=volatile, execute-on-write</code> |
| − | <code | + | <code> soft_trgone 0x00981903 (button) : flags=write-only, execute-on-write</code> |
| − | <code | + | <code> frame_rate 0x00981904 (int) : min=1 max=60 step=1 default=30 value=30 flags=volatile, execute-on-write</code> |
| − | <code | + | <code> roi_x 0x00981905 (int) : min=0 max=1376 step=8 default=0 value=0</code> |
| − | <code | + | <code> roi_y 0x00981906 (int) : min=0 max=1024 step=4 default=0 value=0</code> |
Parameters can be set and get using the following methods. | Parameters can be set and get using the following methods. | ||
| Line 249: | Line 344: | ||
<code>v4l2-ctl --get-ctrl [ctrl_type]</code> | <code>v4l2-ctl --get-ctrl [ctrl_type]</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Note: For Raspberry Pi 5, the -d parameter needs to be added to all commands in this section to specify the subdev used for configuring parameters. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For example, if executing ./media_setting_rpi5.sh or ./find_entity.sh prompts the use of /dev/v4l-subdev2 for parameter configuration, then <code>v4l2-ctl -L</code> should be changed to <code>v4l2-ctl -L -d /dev/v4l-subdev2</code>. | ||
All the above functions can be implemented using [[Mv mipi i2c.sh user guide|mv_mipi_i2c.sh]]. | All the above functions can be implemented using [[Mv mipi i2c.sh user guide|mv_mipi_i2c.sh]]. | ||
| Line 255: | Line 355: | ||
Each of them is described below: | Each of them is described below: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
======Trigger Mode====== | ======Trigger Mode====== | ||
<code>v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl <small>trigger_mode=[0-2]</small></code> | <code>v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl <small>trigger_mode=[0-2]</small></code> | ||
| Line 289: | Line 380: | ||
====== Set ROI ====== | ====== Set ROI ====== | ||
| − | |||
| − | * | + | *method 1,use selection |
| + | |||
| + | <code>v4l2-ctl --set-selection=target=crop,top=0,left=0,width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT</code> | ||
| − | + | Note: This method is not applicable to Raspberry Pi 5. | |
| − | + | The maximum frame rate will be adjusted automatically after setting ROI. | |
| − | <code> | + | *method 2,use user definedroi_x,roi_y and <code>--set-fmt-video</code> |
| − | + | <code>v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl roi_x=0</code> | |
| + | |||
| + | <code>v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl roi_y=0</code> | ||
| + | <code>v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT</code> | ||
==== Video Streaming mode ==== | ==== Video Streaming mode ==== | ||
===== Set ROI ===== | ===== Set ROI ===== | ||
| − | <code>v4l2-ctl --set- | + | <code>v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl roi_x=0</code> |
| + | |||
| + | <code>v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl roi_y=0</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT</code> | ||
===== Set Framerate ===== | ===== Set Framerate ===== | ||
| Line 312: | Line 411: | ||
In streaming mode, the following commands can be used for frame rate statistics. | In streaming mode, the following commands can be used for frame rate statistics. | ||
| − | <code>v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT,pixelformat=GREY --stream-mmap --stream-count=-1 --stream-to=/dev/null</code> | + | <code>v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT,pixelformat=GREY --stream-mmap --stream-count=-1 --stream-to=/dev/null</code> |
===== Save image to file ===== | ===== Save image to file ===== | ||
| Line 365: | Line 464: | ||
<code>v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=2048,height=1544,pixelformat='Y12 ' --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y12-2048x1544.raw</code> | <code>v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=2048,height=1544,pixelformat='Y12 ' --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y12-2048x1544.raw</code> | ||
| + | ======MV-MIPI-IMX264M====== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *raw8 | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=2432,height=2056,pixelformat=GREY --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y8-2432x2056.raw</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *raw10 | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=2432,height=2056,pixelformat='Y10 ' --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y10-2432x2056.raw</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * raw12 | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=2432,height=2056,pixelformat='Y12 ' --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y12-2432x2056.raw</code> | ||
======RAW-MIPI-SC132M====== | ======RAW-MIPI-SC132M====== | ||
* raw8 | * raw8 | ||
| − | <code>v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width= | + | <code>v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=1024,height=1280,pixelformat=GREY --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y8-1024x1280.raw</code> |
| + | |||
| + | *raw10 | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=1024,height=1280,pixelformat='Y10 ' --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y10-1024x1280.raw</code> | ||
| + | ======MV-MIPI-IMX287M====== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *raw8 | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=704,height=544,pixelformat=GREY --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y8-704x544.raw</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * raw10 | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=704,height=544,pixelformat='Y10 ' --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y10-704x544.raw</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *raw12 | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=704,height=544,pixelformat='Y12 ' --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y12-704x544.raw</code> | ||
| + | ====== RAW-MIPI-IMX462M====== | ||
*raw10 | *raw10 | ||
| − | <code>v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width= | + | <code>v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=1920,height=1088,pixelformat='Y10 ' --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y10-1920x1088.raw</code> |
| + | |||
| + | *raw12 | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=1920,height=1088,pixelformat='Y12 ' --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y12-1920x1088.raw</code> | ||
| + | ====== RAW-MIPI-AR0234M====== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *raw8格式 | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=1920,height=1200,pixelformat=GREY --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y8-1920x1200.raw</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *raw10格式 | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=1920,height=1200,pixelformat='Y10 ' --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y10-1920x1200.raw</code> | ||
PS. This y8 file can be used with this player: [https://yuv-player-deluxe.software.informer.com/2.6/ YUV Displayer Deluxe]. | PS. This y8 file can be used with this player: [https://yuv-player-deluxe.software.informer.com/2.6/ YUV Displayer Deluxe]. | ||
| + | =====Preview===== | ||
| + | On a raspberry pi 5, VLC for preview is now having problems and not working. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ======Preview using VLC====== | ||
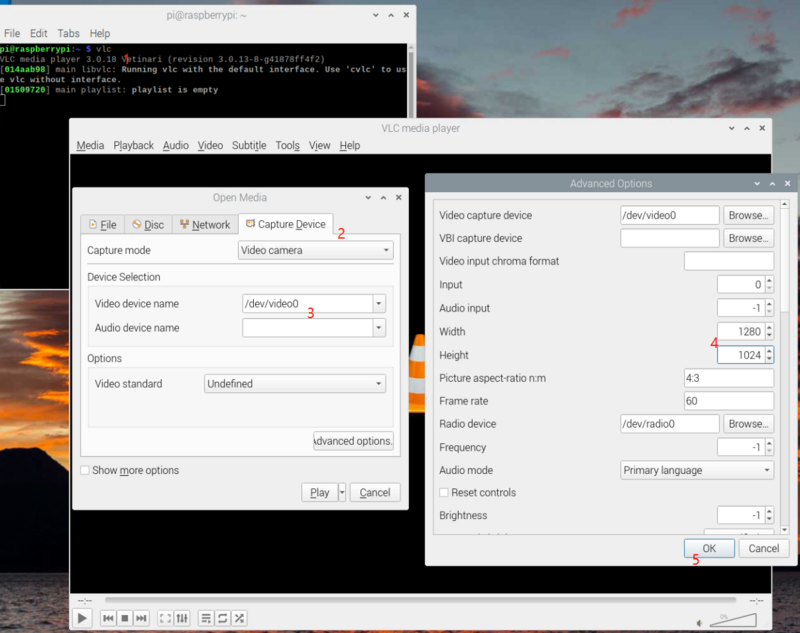
| + | 1. Open VLC with command line <code>vlc</code> , or click the icon to launch. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2. Hit the <code>▶</code>(Play) button to call the open media window. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3. In <code>Capture Device</code> >> <code>Device Selection</code> >> <code>Video device name</code>, select the camera video node. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4. Hit <code>Advanced Options...</code> button | ||
| + | |||
| + | 5. Type in the <code>width</code> and <code>height</code>, for example, 1280 and 1024. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 6. Hit <code>OK</code> to save the settings and see the video feed. | ||
| + | <br />[[File:Mvcam via VLC.png|center|thumb|800x800px|Play mv camera using VLC on RPI|link=http://wiki.veye.cc/index.php/File:Mvcam_via_VLC.png]]<br /> | ||
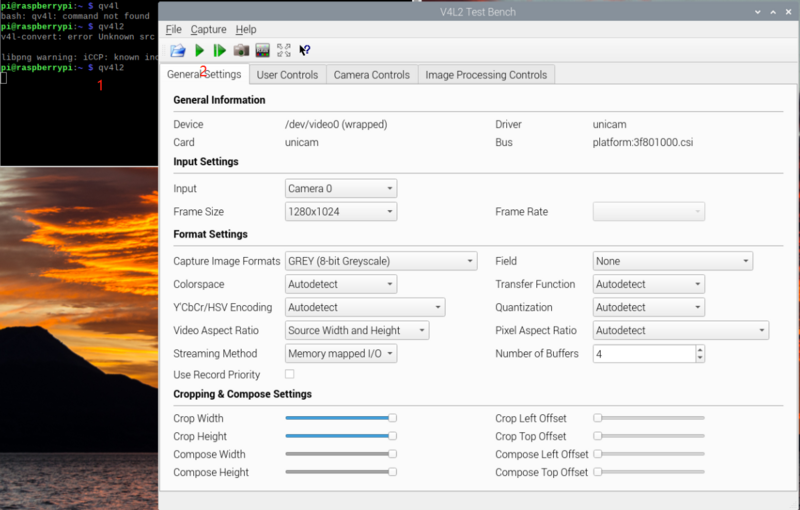
| + | ======Preview using qv4l2====== | ||
| + | Install qv4l2, | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>sudo apt install qv4l2</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1. Open VLC with command line <code>vlc</code> to launch. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2. Hit the <code>▶</code>(Play) button to call the open media window.[[File:Mvcam via qv4l2.png|center|thumb|800x800px|Play mv camera using qv4l2 on RPI|link=http://wiki.veye.cc/index.php/File:Mvcam_via_qv4l2.png]] | ||
| + | ====== Preview UYVY format images using gstreamer ====== | ||
| + | <code>export DISPLAY=:0</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | For easy installation, the MV series cameras provide UYVY mode. The maximum width supported by UYVY mode is 2880, and real-time preview can be performed using the following command. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Note:''' To increase the maximum frame rate and bandwidth, some modules no longer support the UYVY format. Please use the "fmtcap" command in the script to read the registers to confirm the specific configuration. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * install gstreamer | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>sudo apt-get install gstreamer1.0-tools</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>sudo apt-get install libx264-dev libjpeg-dev</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>sudo apt-get install libgstreamer1.0-dev libgstreamer-plugins-base1.0-dev libgstreamer-plugins-bad1.0-dev gstreamer1.0-plugins-ugly gstreamer1.0-tools gstreamer1.0-gl gstreamer1.0-gtk3</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * MV-MIPI-IMX178M | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>v4l2-ctl --set-selection=target=crop,top=0,left=0,width=2816,height=2064</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=/dev/video0 ! "video/x-raw,format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)2816, height=(int)2064, framerate=(fraction)22/1" ! v4l2convert ! "video/x-raw,format=(string)NV12" ! autovideosink sync=false -v</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * MV-MIPI-SC130M, MV-MIPI-IMX296M, MV-MIPI-IMX265M,MV-MIPI-IMX264M,MV-MIPI-IMX287M | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>v4l2-ctl --set-selection=target=crop,top=0,left=0,width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl frame_rate=$FPS</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=/dev/video0 ! "video/x-raw,format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)$WIDTH, height=(int)$HEIGHT,framerate=(fraction)$FPS/1" ! v4l2convert ! "video/x-raw,format=(string)NV12" ! autovideosink sync=false -v</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Or just simply: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=/dev/video0 ! videoconvert ! autovideosink</code> | ||
| + | ====== Preview GREY format images using opencv ====== | ||
| + | |||
| + | * install opencv | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>pip uninstall opencv-python</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>sudo apt install python3-opencv</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Preview using this [https://github.com/veyeimaging/raspberrypi_v4l2/tree/main/samples/opencv/raw_camera sample]: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>python ./v4l2dev_2_opencv_show_grey.py --width 640 --height 480 --fps 30</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | On Raspberry Pi 5, you need to add a <code>--ctldev /dev/v4l-subdev*</code> parameter to specify the subdev for configuring parameters. | ||
==== Trigger mode ==== | ==== Trigger mode ==== | ||
| Line 381: | Line 593: | ||
===== Set ROI and Framerate ===== | ===== Set ROI and Framerate ===== | ||
| − | <code>v4l2-ctl --set- | + | <code>v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl roi_x=0</code> |
| + | |||
| + | <code>v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl roi_y=0</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT</code> | ||
<code>v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl frame_rate=$FPS</code> | <code>v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl frame_rate=$FPS</code> | ||
| Line 418: | Line 634: | ||
Note: script [https://github.com/veyeimaging/mvcam_raspberrypi/tree/main/mv_tools_rpi link]. | Note: script [https://github.com/veyeimaging/mvcam_raspberrypi/tree/main/mv_tools_rpi link]. | ||
| + | ====Notes for CM4 ==== | ||
| + | Cm4 supports the use of two cameras at the same time. Following above steps will only be able to use CAM1. To use two cameras, follow the following steps: | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Hardware Connection ===== | ||
| + | Refer to [https://www.raspberrypi.com/documentation/computers/compute-module.html this Raspberry Pi instruction] , add jumper to J6. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Upgrade dt-blob.bin===== | ||
| + | <code>sudo wget <nowiki>https://datasheets.raspberrypi.com/cmio/dt-blob-dualcam.bin</nowiki> -O /boot/dt-blob.bin</code> | ||
| + | =====For Buster OS(kernel5.10)===== | ||
| + | Upgrade dual camera version dtbo file, use mvcam as an example: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>sudo cp raspberrypi_v4l2/release/driver_bin/$(uname -r)/veye_mvcam-cm4.dtbo /boot/overlays/veye_mvcam.dtbo</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>sudo reboot</code> | ||
| + | =====For Bullseye OS(kernel5.15) ===== | ||
| + | Edit file<code>/boot/config.txt</code>,Add one line<code>dtoverlay=[camera],cam0</code>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Take veye_mvcam as an example. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>[all]</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>dtparam=i2c_vc=on</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>dtoverlay=veye_mvcam</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>dtoverlay=veye_mvcam,cam0</code> | ||
| + | ===== Device node description===== | ||
| + | The CM4 module uses two I2C channels to communicate with the two cameras respectively. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | !description | ||
| + | !i2c bus num | ||
| + | !lane num | ||
| + | !video node | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CAM0 | ||
| + | |0 | ||
| + | |2lane | ||
| + | |video0 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CAM1 | ||
| + | |10 | ||
| + | |2lane or 4lane | ||
| + | |video2(Buster),video1(Bullseye) | ||
| + | |}Note: If there is only one camera, video node is always video0. | ||
====Compiling drivers from source code==== | ====Compiling drivers from source code==== | ||
Please refer to: [http://wiki.veye.cc/index.php/Build_drivers_from_source_for_rpi Build drivers from source for rpi]. | Please refer to: [http://wiki.veye.cc/index.php/Build_drivers_from_source_for_rpi Build drivers from source for rpi]. | ||
| Line 526: | Line 786: | ||
Set rising edge trigger | Set rising edge trigger | ||
| − | <code>./mv_mipi_i2c.sh -w -f trgedge -p1</code> | + | <code>./mv_mipi_i2c.sh -w -f trgedge -p1 0</code> |
In addition, rich trigger attributes can be set for hard triggering, such as trigger delay, signal filtering, etc. | In addition, rich trigger attributes can be set for hard triggering, such as trigger delay, signal filtering, etc. | ||
| Line 535: | Line 795: | ||
<code>python gpio_trigger.py</code> | <code>python gpio_trigger.py</code> | ||
| − | Note: script [https://github.com/veyeimaging/mvcam_raspberrypi/tree/main/mv_tools_rpi link]. | + | Note: script [https://github.com/veyeimaging/mvcam_raspberrypi/tree/main/mv_tools_rpi link].<br /> |
| + | ====Notes for CM4==== | ||
| + | Regarding the descriptions of hardware connections, dtbo, and i2cbus, please refer to the previous sections. | ||
| + | |||
| + | As for accessing two cameras separately using 'mv_raspicam,' the methods are as follows: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Preview CAM0 | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>./mv_raspicam -t -1 -c 0 -y 0</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Preview CAM1 | ||
| − | + | <code>./mv_raspicam -t -1 -c 1 -y 10</code> | |
| + | === Raw data format === | ||
==== Unpacked image format(padded) ==== | ==== Unpacked image format(padded) ==== | ||
| Line 573: | Line 844: | ||
===i2c script for parameter configuration=== | ===i2c script for parameter configuration=== | ||
We provide shell scripts to configure the parameters. | We provide shell scripts to configure the parameters. | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://github.com/veyeimaging/raspberrypi_v4l2/tree/main/mv_tools_rpi | ||
[http://wiki.veye.cc/index.php/Mv_mipi_i2c.sh_user_guide mv_mipi_i2c.sh user guide] | [http://wiki.veye.cc/index.php/Mv_mipi_i2c.sh_user_guide mv_mipi_i2c.sh user guide] | ||
| Line 581: | Line 854: | ||
=== Document History === | === Document History === | ||
| + | |||
| + | * 2024-01-01 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Add support for Raspberrypi 5. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *2023-08-16 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Add support for RAW-MIPI-IMX462M and RAW-MIPI-AR0234M. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * 2023-06-07 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Add preview method using qv4l2 and VLC. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * 2023-04-14 | ||
| + | |||
| + | With the new version of the driver, the flip operation has been removed, and a new ROI configuration method has been added. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * 2023-03-29 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Add opencv samples. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *2023-03-26 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Add support for MV-MIPI-IMX287M. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *2023-03-04 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Add the instructions related to CM4 in Bullseye system. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * 2023-02-10 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Add note for CM4. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * 2022-12-08 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Add support for the new MV-MIPI-IMX264M camera model. | ||
* 2022-11-02 | * 2022-11-02 | ||
| − | + | Add support for the new IMX265 and SC132 models. | |
* 2022-05-16 | * 2022-05-16 | ||
Revision as of 09:23, 25 January 2024
1 Overview
The MV series cameras are cameras introduced for AI applications in the industrial field. It uses the MIPI CSI-2 interface, which is especially suitable for embedded computing platforms.
It features rich data formats and trigger characteristics, extremely low latency, extremely high bandwidth and reliable stability.
This article describes how to use the MV series camera on the Raspberry Pi platform.
1.1 Camera module list
| Series | Model | Status |
|---|---|---|
| MV series | MV-MIPI-IMX178M | Done |
| MV series | MV-MIPI-SC130M | Done |
| MV series | MV-MIPI-IMX296M | Done |
| MV series | MV-MIPI-IMX287M | Done |
| MV series | MV-MIPI-IMX265M | Done |
| MV series | MV-MIPI-IMX264M | Done |
| RAW series | RAW-MIPI-SC132M | Done |
| RAW series | RAW-MIPI-IMX462M | Done |
| RAW series | RAW-MIPI-AR0234M | Done |
2 Hardware Setup
2.1 MV series cameras use the ADP-MV1 connection
MV series cameras need to use ADP-MV1 adapter board in order to connect to Raspberry Pi.
2.1.1 Connection of MV series camera and ADP-MV1
The two are connected using 0.5 mm pitch*30P FFC cable with opposite-side contacts. The cable must be inserted with the silver contacts facing outside.
| TOP | BOTTOM |
|---|---|
2.1.2 Power supply
The ADP-MV1 requires a separate 5V power supply and can be powered directly from the Raspberry Pi motherboard using a Dupont cable.
2.1.3 Raspberry Pi 5
The two are connected using 15Pto22P FFC cable with Same-side contacts. Pay attention to the silver contacts facing side.
2.1.4 Raspberry Pi Model B and B+
The two are connected using 1.0 mm pitch*15P FFC cable with opposite-side contacts. Pay attention to the silver contacts facing side.
2.1.5 Raspberry Pi Zero, Zero W and Computer Module
The two are connected using 15Pto22P FFC cable with Same-side contacts. Pay attention to the silver contacts facing side.
2.2 RAW series cameras directly connected to Raspberrypi
2.2.1 Raspberry Pi 5
The RAW-MIPI-SC132M use a 15-to-22-pin same-side FFC cable, while other RAW series cameras use a 22-pin opposite-side FFC cable.
2.2.2 Raspberry Pi Model B and B+
The RAW-MIPI-SC132M use a 15-pin opposite-side FFC cable, while other RAW series cameras use a 15-to-22-pin same-side FFC cable.
2.2.3 Raspberry Pi Zero, Zero W and Computer Module
The RAW-MIPI-SC132M use a 15-to-22-pin same-side FFC cable, while other RAW series cameras use a 22-pin opposite-side FFC cable.
3 piOS Configuration
For details on how to install the Raspberry Pi system, please refer to the official documentation at Install raspberry pi guide.
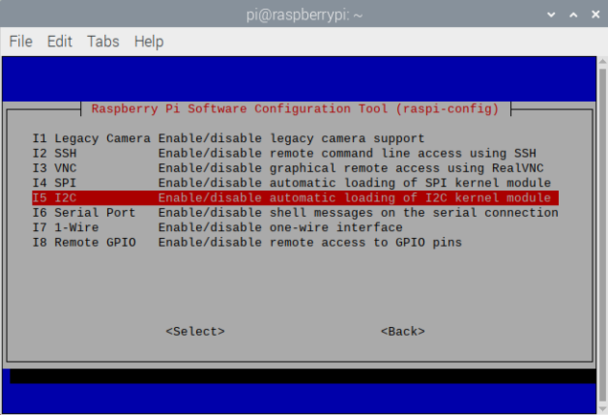
Initially, the Raspberry Pi system I2C is not enabled. After booting, we need to turn them on manually by executing the following command:
sudo raspi-config
Enter Interface Options, enable I2C, and then restart the Raspberry Pi.
It is recommended to enable the ssh service and samba service of Raspberry Pi system, here we will not go into the details of how to enable ssh and samba service of Raspberry Pi system.
4 V4L2 mode and Legacy mode introduction
In the latest Raspberry Pi Bookworm system, support for Legacy mode has been removed. It is recommended for customers to use the V4L2 mode.
4.1 libcamera and V4L2 mode
Now piOS has switched to libcamera-stack mode.
Libcamera is essentially centered on implementing isp functionality, something that is not needed for the MV series cameras. Therefore, we have adopted the V4L2 mode instead of using libcamera-stack.
As with libcamera-stack, our V4L2 model implements the standard V4L2 driver for the linux driver layer too. Based on this driver, the application layer can directly develop programs to acquire images and perform further processing.
4.2 Legacy mode
Traditional mode, relying on Broadcom's GPU for image processing. The traditional raspicam software set uses this model.
The disadvantage of this model is closed. The GPU side is closed source, can not freely access sensor.
The Raspberry Pi organization has switched to the libcamera camera stack, but this model still has value:
- More use of GPU resources and lower CPU load. This is useful for earlier versions of the Raspberry Pi where CPU performance is poorer.
- It is possible to simply and directly fetch image data to the application layer without the support of the driver layer. This is especially useful for cameras that do not rely on the Raspberry Pi's isp.
- libcamera lacks some feature support now.
There are two ways to use Legacy mode.
- Use the Legacy version of piOS.
- For the bullseye or newer version of piOS, turn on the Legacy Camera option in raspi-config.
Since the two modes cannot co-exist, Legacy mode needs to be turned off when using V4L2 mode.
5 Configuring global variables
For the convenience of later descriptions, global variables are configured here according to the sensor size.
- MV-MIPI-IMX178M
export WIDTH=3088
export HEIGHT=2064
export FPS=22
- MV-MIPI-SC130M
export WIDTH=1280
export HEIGHT=1024
export FPS=108
- MV-MIPI-IMX296M
export WIDTH=1440
export HEIGHT=1088
export FPS=60
- MV-MIPI-IMX287M
export WIDTH=704
export HEIGHT=544
export FPS=319
- MV-MIPI-IMX265M
export WIDTH=2048
export HEIGHT=1544
export FPS=45
- MV-MIPI-IMX264M
export WIDTH=2432
export HEIGHT=2056
export FPS=28
- RAW-MIPI-SC132M
export WIDTH=1024
export HEIGHT=1280
export FPS=120
- RAW-MIPI-IMX462M
export WIDTH=1920
export HEIGHT=1088
export FPS=60
- RAW-MIPI-AR0234M
export WIDTH=1920
export HEIGHT=1200
export FPS=60
6 V4L2 mode manual
We have saved the code for v4l2 mode in this github repository.
6.1 Download the driver package
wget https://github.com/veyeimaging/raspberrypi_v4l2/releases/latest/download/raspberrypi_v4l2.tgz
6.2 Install driver
tar -xzvf raspberrypi_v4l2.tgz
cd raspberrypi_v4l2/release/
chmod +x *
- For Raspberry Pi 5
sudo ./install_driver_rpi5.sh veye_mvcam
It will install both CAM1 and CAM0 overlays in /boot/config.txt.
- For other Raspberry Pi
sudo ./install_driver.sh veye_mvcam
Then reboot Raspberry Pi.
Note: If you are prompted that the corresponding version of the driver cannot be found, it means that we do not provide a compiled driver corresponding to your piOS version. Please try to compile from the source code.
6.3 Uninstall the driver
If you need to change to Legacy mode, or want to change to another camera module model driver, you must uninstall the current driver first.
sudo ./uninstall_driver.sh veye_mvcam
6.4 Check system status
Take MV-MIPI-IMX178M as an example.
dmesg | grep mvcam
You can see the camera model and the version of the camera probed during the Linux boot phase.
camera is: MV-MIPI-IMX178M
firmware version: 0x1080102
And the /dev/video0 node exists, which proves that the camera status is normal.
6.5 Raspberry Pi 5 Setting
On Raspberry Pi 5,the drivers now use the media controller API, and we must setup the media graph correctly first. This includes setting up the media pad formats correctly and correctly linking them together.
We provide a series of scripts to implement this functionality, saved in the rpi5_scripts directory.
- ./find_entity.sh
$ ./find_entity.sh
Found mvcam @ i2c-4 entity on /dev/media3
Plese get frame from /dev/video0 and use /dev/v4l-subdev2 for camera setting.
Found mvcam @ i2c-6 entity on /dev/media0
Plese get frame from /dev/video8 and use /dev/v4l-subdev5 for camera setting.
After a reboot of Raspberry Pi 5, the media node and video node of the camera may change. Therefore, it is recommended to execute ./find_entity.sh before performing subsequent operations to identify the device nodes.
The above prompt shows that the system has detected two cameras and their corresponding device nodes.
i2c-4 corresponds to the CAM1 port on the board, and i2c-6 corresponds to the CAM0 port on the board.
- media_setting_rpi5.sh
./media_setting_rpi5.sh
Usage: ./media_setting_rpi5.sh veyecam2m/csimx307/cssc132/mvcam -fmt [UYVY/RAW8/RAW10/RAW12] -w [width] -h [height]
This shell script is designed to detect the connection of a camera on Raspberry Pi 5.
It utilizes media-ctl and v4l2-ctl commands to configure the linking relationships and data formats of the media pad.
Once completed, you can directly use /dev/video0 or /dev/video8 to obtain image data
Before proceeding with further operations, it is necessary to execute this script to complete the configuration of parameters.
For instance,RAW-MIPI-AR0234M:
./media_setting_rpi5.sh mvcam -fmt RAW8 -w 1920 -h 1200
6.6 v4l2-ctl application examples
6.6.1 Install v4l2-utils
sudo apt-get install v4l-utils
6.6.2 Install yavta
git clone git://git.ideasonboard.org/yavta.git
cd yavta;make
6.6.3 Configure parameters using v4l2-ctl
6.6.3.1 List the data formats supported by the camera
v4l2-ctl --list-formats-ext
ioctl: VIDIOC_ENUM_FMT
Type: Video Capture
[0]: 'GREY' (8-bit Greyscale)
Size: Discrete 3088x2064
[1]: 'Y10P' (10-bit Greyscale (MIPI Packed))
Size: Discrete 3088x2064
[2]: 'Y10 ' (10-bit Greyscale)
Size: Discrete 3088x2064
[3]: 'Y12P' (12-bit Greyscale (MIPI Packed))
Size: Discrete 3088x2064
[4]: 'Y12 ' (12-bit Greyscale)
Size: Discrete 3088x2064
On Raspberry Pi 5, the actual supported image formats depend on the capabilities of the camera, not the list provided here.
6.6.3.2 List the configurable parameters of the camera implemented in the driver
v4l2-ctl -L
User Controls
trigger_mode 0x00981901 (int) : min=0 max=2 step=1 default=0 value=0 flags=volatile, execute-on-write
trigger_src 0x00981902 (int) : min=0 max=1 step=1 default=1 value=1 flags=volatile, execute-on-write
soft_trgone 0x00981903 (button) : flags=write-only, execute-on-write
frame_rate 0x00981904 (int) : min=1 max=60 step=1 default=30 value=30 flags=volatile, execute-on-write
roi_x 0x00981905 (int) : min=0 max=1376 step=8 default=0 value=0
roi_y 0x00981906 (int) : min=0 max=1024 step=4 default=0 value=0
Parameters can be set and get using the following methods.
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl [ctrl_type]=[val]
v4l2-ctl --get-ctrl [ctrl_type]
Note: For Raspberry Pi 5, the -d parameter needs to be added to all commands in this section to specify the subdev used for configuring parameters.
For example, if executing ./media_setting_rpi5.sh or ./find_entity.sh prompts the use of /dev/v4l-subdev2 for parameter configuration, then v4l2-ctl -L should be changed to v4l2-ctl -L -d /dev/v4l-subdev2.
All the above functions can be implemented using mv_mipi_i2c.sh.
None of the above parameters can be modified in the state when the image acquisition is started.
Each of them is described below:
6.6.3.3 Trigger Mode
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl trigger_mode=[0-2]
0:Video streaming mode
1:Normal trigger mode.
2:High-speed continuous trigger mode.
6.6.3.4 Trigger Source
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl trigger_src=[0-1]
0: Software trigger mode.
1: Hardware trigger mode.
6.6.3.5 Software trigger command
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl soft_trgone=1
6.6.3.6 Set frame rate
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl frame_rate=[1-max]
The maximum frame rate is automatically updated as the resolution changed.
6.6.3.7 Set ROI
- method 1,use selection
v4l2-ctl --set-selection=target=crop,top=0,left=0,width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT
Note: This method is not applicable to Raspberry Pi 5.
The maximum frame rate will be adjusted automatically after setting ROI.
- method 2,use user definedroi_x,roi_y and
--set-fmt-video
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl roi_x=0
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl roi_y=0
v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT
6.7 Video Streaming mode
6.7.1 Set ROI
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl roi_x=0
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl roi_y=0
v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT
6.7.2 Set Framerate
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl frame_rate=$FPS
6.7.3 Frame rate statistics
In streaming mode, the following commands can be used for frame rate statistics.
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT,pixelformat=GREY --stream-mmap --stream-count=-1 --stream-to=/dev/null
6.7.4 Save image to file
6.7.4.1 MV-MIPI-IMX178M
- raw8
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=3088,height=2064,pixelformat=GREY --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y8-3104x2064.raw
Or
./yavta -c1 -Fy8-3104x2064.raw --skip 0 -f Y8 -s 3088x2064 /dev/video0
Since the memory requested by Raspberry Pi for the image, the width is 32-align and the height is 16-align, the 3088*2064 image will be saved as 3104*2064 size.
- raw10
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=3088,height=2064,pixelformat='Y10 ' --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y10-3088x2064.raw
- raw12
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=3088,height=2064,pixelformat='Y12 ' --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y12-3088x2064.raw
6.7.4.2 MV-MIPI-SC130M
- raw8
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=1280,height=1024,pixelformat=GREY --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y8-1280x1024.raw
- raw10
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=1280,height=1024,pixelformat='Y10 ' --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y10-1280x1024.raw
6.7.4.3 MV-MIPI-IMX296M
- raw8
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=1440,height=1088,pixelformat=GREY --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y8-1440x1088.raw
- raw10
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=1440,height=1088,pixelformat='Y10 ' --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y10-1440x1088.raw
6.7.4.4 MV-MIPI-IMX265M
- raw8
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=2048,height=1544,pixelformat=GREY --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y8-2048x1544.raw
- raw10
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=2048,height=1544,pixelformat='Y10 ' --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y10-2048x1544.raw
- raw12
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=2048,height=1544,pixelformat='Y12 ' --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y12-2048x1544.raw
6.7.4.5 MV-MIPI-IMX264M
- raw8
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=2432,height=2056,pixelformat=GREY --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y8-2432x2056.raw
- raw10
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=2432,height=2056,pixelformat='Y10 ' --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y10-2432x2056.raw
- raw12
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=2432,height=2056,pixelformat='Y12 ' --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y12-2432x2056.raw
6.7.4.6 RAW-MIPI-SC132M
- raw8
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=1024,height=1280,pixelformat=GREY --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y8-1024x1280.raw
- raw10
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=1024,height=1280,pixelformat='Y10 ' --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y10-1024x1280.raw
6.7.4.7 MV-MIPI-IMX287M
- raw8
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=704,height=544,pixelformat=GREY --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y8-704x544.raw
- raw10
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=704,height=544,pixelformat='Y10 ' --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y10-704x544.raw
- raw12
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=704,height=544,pixelformat='Y12 ' --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y12-704x544.raw
6.7.4.8 RAW-MIPI-IMX462M
- raw10
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=1920,height=1088,pixelformat='Y10 ' --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y10-1920x1088.raw
- raw12
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=1920,height=1088,pixelformat='Y12 ' --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y12-1920x1088.raw
6.7.4.9 RAW-MIPI-AR0234M
- raw8格式
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=1920,height=1200,pixelformat=GREY --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y8-1920x1200.raw
- raw10格式
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=1920,height=1200,pixelformat='Y10 ' --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=y10-1920x1200.raw
PS. This y8 file can be used with this player: YUV Displayer Deluxe.
6.7.5 Preview
On a raspberry pi 5, VLC for preview is now having problems and not working.
6.7.5.1 Preview using VLC
1. Open VLC with command line vlc , or click the icon to launch.
2. Hit the ▶(Play) button to call the open media window.
3. In Capture Device >> Device Selection >> Video device name, select the camera video node.
4. Hit Advanced Options... button
5. Type in the width and height, for example, 1280 and 1024.
6. Hit OK to save the settings and see the video feed.
6.7.5.2 Preview using qv4l2
Install qv4l2,
sudo apt install qv4l2
1. Open VLC with command line vlc to launch.
2. Hit the ▶(Play) button to call the open media window.
6.7.5.3 Preview UYVY format images using gstreamer
export DISPLAY=:0
For easy installation, the MV series cameras provide UYVY mode. The maximum width supported by UYVY mode is 2880, and real-time preview can be performed using the following command.
Note: To increase the maximum frame rate and bandwidth, some modules no longer support the UYVY format. Please use the "fmtcap" command in the script to read the registers to confirm the specific configuration.
- install gstreamer
sudo apt-get install gstreamer1.0-tools
sudo apt-get install libx264-dev libjpeg-dev
sudo apt-get install libgstreamer1.0-dev libgstreamer-plugins-base1.0-dev libgstreamer-plugins-bad1.0-dev gstreamer1.0-plugins-ugly gstreamer1.0-tools gstreamer1.0-gl gstreamer1.0-gtk3
- MV-MIPI-IMX178M
v4l2-ctl --set-selection=target=crop,top=0,left=0,width=2816,height=2064
gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=/dev/video0 ! "video/x-raw,format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)2816, height=(int)2064, framerate=(fraction)22/1" ! v4l2convert ! "video/x-raw,format=(string)NV12" ! autovideosink sync=false -v
- MV-MIPI-SC130M, MV-MIPI-IMX296M, MV-MIPI-IMX265M,MV-MIPI-IMX264M,MV-MIPI-IMX287M
v4l2-ctl --set-selection=target=crop,top=0,left=0,width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl frame_rate=$FPS
gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=/dev/video0 ! "video/x-raw,format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)$WIDTH, height=(int)$HEIGHT,framerate=(fraction)$FPS/1" ! v4l2convert ! "video/x-raw,format=(string)NV12" ! autovideosink sync=false -v
Or just simply:
gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=/dev/video0 ! videoconvert ! autovideosink
6.7.5.4 Preview GREY format images using opencv
- install opencv
pip uninstall opencv-python
sudo apt install python3-opencv
- Preview using this sample:
python ./v4l2dev_2_opencv_show_grey.py --width 640 --height 480 --fps 30
On Raspberry Pi 5, you need to add a --ctldev /dev/v4l-subdev* parameter to specify the subdev for configuring parameters.
6.8 Trigger mode
This section takes IMX178 as an example to show the configuration and use of trigger mode. For other cameras, just refer to the width and height of the stream mode.
6.8.1 Set ROI and Framerate
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl roi_x=0
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl roi_y=0
v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl frame_rate=$FPS
6.8.2 Software trigger mode
6.8.2.1 Set mode
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl trigger_mode=1
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl trigger_src=0
6.8.2.2 Start acquisition
v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=3088,height=2064,pixelformat=GREY --stream-mmap --stream-count=5 --stream-to=y8-3104x2064.yuv
6.8.2.3 Perform soft trigger operation
In other shell terminals, you can execute the following command multiple times for multiple triggers.
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl soft_trgone=1
6.8.3 Hardware trigger mode
The following is an example of using Raspberry Pi GPIO21 as an trigger source with rising edge trigger.
You can use the mv_mipi_i2c.sh script for other trigger parameter setting.
6.8.3.1 Hardware Connection
6.8.3.2 Set mode
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl trigger_mode=1
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl trigger_src=1
6.8.3.3 Start acquisition
v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=3088,height=2064,pixelformat=GREY --stream-mmap --stream-count=5 --stream-to=y8-3104x2064.yuv
6.8.3.4 Perform hardware trigger operation
python gpio_trigger.py
Note: script link.
6.9 Notes for CM4
Cm4 supports the use of two cameras at the same time. Following above steps will only be able to use CAM1. To use two cameras, follow the following steps:
6.9.1 Hardware Connection
Refer to this Raspberry Pi instruction , add jumper to J6.
6.9.2 Upgrade dt-blob.bin
sudo wget https://datasheets.raspberrypi.com/cmio/dt-blob-dualcam.bin -O /boot/dt-blob.bin
6.9.3 For Buster OS(kernel5.10)
Upgrade dual camera version dtbo file, use mvcam as an example:
sudo cp raspberrypi_v4l2/release/driver_bin/$(uname -r)/veye_mvcam-cm4.dtbo /boot/overlays/veye_mvcam.dtbo
sudo reboot
6.9.4 For Bullseye OS(kernel5.15)
Edit file/boot/config.txt,Add one linedtoverlay=[camera],cam0.
Take veye_mvcam as an example.
[all]
dtparam=i2c_vc=on
dtoverlay=veye_mvcam
dtoverlay=veye_mvcam,cam0
6.9.5 Device node description
The CM4 module uses two I2C channels to communicate with the two cameras respectively.
| description | i2c bus num | lane num | video node |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAM0 | 0 | 2lane | video0 |
| CAM1 | 10 | 2lane or 4lane | video2(Buster),video1(Bullseye) |
Note: If there is only one camera, video node is always video0.
6.10 Compiling drivers from source code
Please refer to: Build drivers from source for rpi.
7 Legacy mode manual
We store the code for legacy patterns in this github repository.
7.1 Download the software package
git clone https://github.com/veyeimaging/mvcam_raspberrypi.git
Add executable permissions:
chmod +x -R ./mvcam_raspberrypi/
7.2 Software package main content introduction
camera_i2c_config:Automatically recognizes different Raspberry Pi board types and controls the power on pins to power the camera.
mv_raspicam:Realize image preview, image saving and other functions.
mv_mipi_i2c.sh:Scripts for reading and setting camera parameters via i2c protocol.
veye_i2c_upgrade:Camera firmware upgrade tool.
7.3 Camera power on
./camera_i2c_config
When the camera is powered on, try:
i2cdetect -y 10
The presence of a 0x3b device indicates that the camera is on and the i2c channel is working properly.
7.4 Preview
./mv_raspicam -t -1 -roi 0,0,3088,2064 -md 0
where -md specifies the pixel data format.
| -md option | data type |
|---|---|
| 0 | 8bit Y |
| 1 | 10bit Y |
| 2 | 12bit Y |
-roi specifies the desired ROI size.
For sizes larger than 1920 in width, mv_raspicam will first reduce to half the original size of the image and then send to render.
7.5 Save image
./mv_raspicam -t 1000 -roi 0,0,3088,2064 -md 0 -sr 10 -o /dev/shm/y8-3104x2064_%04d.yuv
-sr is the interval for storing images, one image is saved every 10 images here.
-t 1000, in ms, it means 1 second here.
Several files will be saved in the /dev/shm/ directory after completion.
7.6 Trigger mode
This section requires the use of mv_mipi_i2c.sh, please refer to the related i2c parameter configuration section below.
7.6.1 Software trigger mode
7.6.1.1 Set mode
./mv_mipi_i2c.sh -w -f trgmode -p1 1
./mv_mipi_i2c.sh -w -f trgsrc -p1 0
7.6.1.2 Set trigger properties
You can set the number of triggers, trigger interval, etc.
The following settings are for a single trigger of 5 images with an interval of 1 second each.
./mv_mipi_i2c.sh -w -f trgnum -p1 5
./mv_mipi_i2c.sh -w -f trginterval -p1 1000
7.6.1.3 Start acquisition
./mv_raspicam -t -1 -roi 0,0,3088,2064 -md 0
7.6.1.4 Perform soft trigger operation
In other shell terminals, you can execute the following command multiple times for multiple triggers.
./mv_mipi_i2c.sh -w -f trgone
7.6.2 Hardware trigger mode
The following is an example of using Raspberry Pi GPIO21 as an trigger source with rising edge trigger.
You can use the mv_mipi_i2c.sh script for other trigger parameter setting.
7.6.2.1 Hardware Connection
7.6.2.2 Set mode
This time, we use high-speed continuous trigger as an example.
./mv_mipi_i2c.sh -w -f trgmode -p1 2
./mv_mipi_i2c.sh -w -f trgsrc -p1 1
7.6.2.3 Set trigger properties
The trigger interval is invalid under high-speed continuous triggering. This time trigger 2 images.
./mv_mipi_i2c.sh -w -f trgnum -p1 2
Set rising edge trigger
./mv_mipi_i2c.sh -w -f trgedge -p1 0
In addition, rich trigger attributes can be set for hard triggering, such as trigger delay, signal filtering, etc.
7.6.2.4 Start acquisition
./mv_raspicam -t -1 -roi 0,0,3088,2064 -md 0
7.6.2.5 Perform hardware trigger operation
python gpio_trigger.py
Note: script link.
7.7 Notes for CM4
Regarding the descriptions of hardware connections, dtbo, and i2cbus, please refer to the previous sections.
As for accessing two cameras separately using 'mv_raspicam,' the methods are as follows:
- Preview CAM0
./mv_raspicam -t -1 -c 0 -y 0
- Preview CAM1
./mv_raspicam -t -1 -c 1 -y 10
8 Raw data format
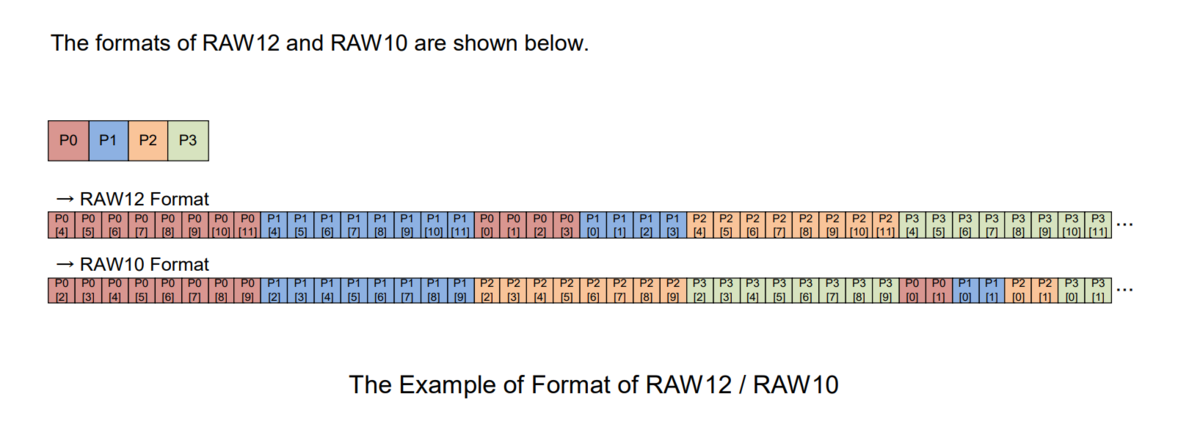
8.1 Unpacked image format(padded)
For 10bit depth and 12bit depth pixel data, two bytes are always used to store one pixel. The V4L2 standard 'Y10 ' (10-bit Greyscale),'Y12 ' (12-bit Greyscale)formats are stored in this way.
This storage method is convenient for software processing, but has the disadvantage of taking up more space.
8.2 Packed image format
The data format saved by mv_raspicam is the data format on the MIPS bus, with no empty bit padding between pixels.
The V4L2 standard'Y10P' (10-bit Greyscale (MIPI Packed)),'Y12P' (12-bit Greyscale (MIPI Packed))formats are stored in this way.
8.3 Packed image size
Buffersize= ALIGN_UP(width*bit_depth/8,32)*ALIGN_UP(height,16)
The row buffer size should be 32 bytes aligned; the column buffer size should be 16 bytes aligned.
For example, the image size of 3088*2064@8bit is 6406656; the image size of 3088*2064@10bit is 7991808; the image size of 3088*2064@12bit is 9576960.
8.4 Format convert tool
We have written a small tool: pixel_layer_convert, which can easily convert packed images to unpacked images.
For example, the following command converts a packed raw10 image of 3088 width to an unpacked raw10.
./pixel_layer_convert -I Y10P -i y10-3088x2064_0001.raw -o y10-3088x2064_0001_new.raw -w 3088
8.5 Raw data image player
We recommend using vooya as the player, which supports GREY, and unpacked image formats.
Also, y8 file can be used with this player: YUV Displayer Deluxe.
Since the memory requested by Raspberry Pi for the image, the width is 32-align and the height is 16-align, the 3088*2064 image will be saved as 3104*2064 size.
9 i2c script for parameter configuration
We provide shell scripts to configure the parameters.
https://github.com/veyeimaging/raspberrypi_v4l2/tree/main/mv_tools_rpi
10 References
- Installation of the Raspberry Pi system
- The difference between Raspberry Pi legacy camera stack and libcamera mode
11 Document History
- 2024-01-01
Add support for Raspberrypi 5.
- 2023-08-16
Add support for RAW-MIPI-IMX462M and RAW-MIPI-AR0234M.
- 2023-06-07
Add preview method using qv4l2 and VLC.
- 2023-04-14
With the new version of the driver, the flip operation has been removed, and a new ROI configuration method has been added.
- 2023-03-29
Add opencv samples.
- 2023-03-26
Add support for MV-MIPI-IMX287M.
- 2023-03-04
Add the instructions related to CM4 in Bullseye system.
- 2023-02-10
Add note for CM4.
- 2022-12-08
Add support for the new MV-MIPI-IMX264M camera model.
- 2022-11-02
Add support for the new IMX265 and SC132 models.
- 2022-05-16
Provide image format convert tool.
- 2022-04-14
Release 1st version.