Difference between revisions of "GX series camera appnotes 4 jetson"
(→触发模式) |
|||
| Line 447: | Line 447: | ||
Note:触发脚本[https://github.com/veyeimaging/nvidia_jetson_veye_bsp/tree/master/mv_tools_jetson/examples/v4l2grab_mvcam 链接]。 | Note:触发脚本[https://github.com/veyeimaging/nvidia_jetson_veye_bsp/tree/master/mv_tools_jetson/examples/v4l2grab_mvcam 链接]。 | ||
| − | ====== | + | ======Stop triggering and collecting====== |
| − | + | Due to the fact that in the kernel driver, a dead loop is used to wait for new images, it is necessary to first disable vi_time_out_disable, and then exit the acquisition operation. | |
<code>v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl vi_time_out_disable=0</code> | <code>v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl vi_time_out_disable=0</code> | ||
| − | + | In the terminal of the image acquisition command, press Ctrl+C to exit the acquisition operation. | |
| − | ==== | + | ====synchronous mode==== |
| − | ===== | + | =====Set the synchronization mode===== |
<code>$ v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl work<small>_mode=4</small></code> | <code>$ v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl work<small>_mode=4</small></code> | ||
| − | ===== | + | =====Set up the master and slave cameras===== |
| − | + | Main camera: | |
<code>$ v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl <small>sync_role=0</small></code> | <code>$ v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl <small>sync_role=0</small></code> | ||
| − | + | slave camera: | |
<code>$ v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl <small>sync_role=1</small></code> | <code>$ v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl <small>sync_role=1</small></code> | ||
| − | ===== | + | =====Start taking pictures===== |
| − | + | The method of taking screenshots in the synchronization mode is exactly the same as that in the video stream mode. | |
| − | === | + | ===I2C Script Usage Instructions=== |
| − | + | We provided shell scripts to configure the parameters. | |
| − | [https://wiki.veye.cc/index.php/Gx_mipi_i2c.sh_user_guide | + | [https://wiki.veye.cc/index.php/Gx_mipi_i2c.sh_user_guide gx_mipi_i2c.sh user guide] |
===参考资料=== | ===参考资料=== | ||
===本文修改记录=== | ===本文修改记录=== | ||
Revision as of 10:45, 18 December 2025
1 overview
The GX series cameras are designed for embedded AI applications, featuring outstanding ISP performance, multiple working modes, a wealth of functional options, and reliable stability design. They use the MIPI CSI-2 interface and are particularly suitable for embedded computing platforms.
This article introduces how to use GX series cameras on the NVIDIA Jetson platform.
1.1 Supported camera modules
| series | model | status |
|---|---|---|
| GX Series | GX-MIPI-IMX662 | complete |
1.2 Supported Jetson Board
| Jetson model | status |
|---|---|
| XAVIER NX | complete |
| Orin NX | complete |
| Orin Nano | complete |
1.3 Supported L4T versions
- Jetpack5.1.4,L4T version r35.6
- Jetpack6.2.1,L4T version r36.4.4
1.3.1 How to check the current L4T version
On the Jetson board, check the current L4T version and try to replace it with the same version.
cat /etc/nv_tegra_release
As shown:
# R32 (release), REVISION: 7.1......
This indicates that the current L4T version is 32.7.1, and the corresponding Jetpack version is Jetpack 32.6.1.
2 Hardware preparation and installation
The GX series cameras require a adapter board to be connected to the Jetson platform. The supported conditions are as shown in the table below:
| Camera model | Jetson model | FFC line | Number of cameras | Additional power supply |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GX Series | XAVIER NX | 15-pin to 22-pin face-to-face FFC conversion connector | 2 | 5V DC (must be provided) |
| Orin Nano
Orin NX |
22-pin oblique FFC | 2 | 5V DC (must be provided) |
2.1 GX camera connected to Xavier NX
TBD
2.2 The GX camera is connected to Orin Nano or Orin NX.
TBD
3 Update the Jetson system
This section describes how to update the L4T system of Jetson to support the GX camera module. For the method of operating system update, please refer to the update instructions for Jetson operating system.
In particular, if you need the external trigger function, you need to apply a patch to the original kernel of Jetson - veye_mv_l4t_<version>.patch.
This patch has two functions:
- Added support for two data formats, Y10 and Y12, for black-and-white cameras.
- Added support for the trigger mode.
4 Support for the Trigger mode
The default driver of the Jetson system only supports video streaming mode. In its VI driver, the data reception function has a timeout mechanism. We have added a configurable option named "vi_time_out_disable" which allows for dynamically enabling or disabling this timeout mechanism.
For specific applications, please refer to the following application examples.
5 System status monitoring
After completing the system update, restart the Jetson motherboard.
During the startup process of the Jetson system, it will check whether there are any cameras on all i2c buses. If there are, it will create a /dev/videoX device node.
Execute the following commands on the Jetson board to check if the camera is properly connected.
dmesg | grep gxcam
It can be seen that during the Linux startup process, the camera model and version number that were probed are as follows:
For example, the following prompt indicates that a GX-MIPI-IMX662 camera has been detected on the i2c-9 bus.
gxcam 9-003b: camera is: GX-MIPI-IMX662
6 Detect the status and configure the environment variables
Here, we have provided two scripts that can automatically retrieve some information about the camera.
6.1 probe_camera_info-jetson.sh
This script is used to detect the connected and successfully registered camera devices, and retrieve the underlying information such as the media device nodes, video device nodes, sub-device nodes, I²C bus and device names corresponding to the devices.
After execution, an "auto_camera_index.json" file will be generated in the current directory, and the retrieved information will be recorded in this file.
Here is an example:
$ ./probe_camera_info-jetson.sh
cat auto_camera_index.json
[
{"i2c_bus": "9", "video_node": "/dev/video0"}
]
{}Inside is the information of the camera. If the motherboard supports multiple camera modules, then multiple sets of {} will contain the content.
The explanation of the camera information is as follows:
| antonomasia | name | effect | Where to use |
|---|---|---|---|
| video_node | Video capture device node | Typical V4L2 video device | v4l2-ctl or the programs developed by the customers are used to obtain the images. |
| i2c_bus | I²C bus number | The I²C bus number indicating the device connection | The underlying communication channel for configuring the camera parameters, the gx_mipi_i2c.sh script uses |
The media device nodes, video device nodes, sub-device nodes, I²C bus and device names used in the following text can all be replaced with the information in the JSON file obtained from this detection script.
The camera module is mapped to the /dev/videoX device node in the Jetson system.
During the startup process of the operating system, the cameras are probed in the order of the i2c bus from small to large. The X value starts from 0 and increments in the logical order of the probe.
For example, if only one camera is connected, regardless of where the hardware is connected, X will be 0. If five cameras are connected, then according to the i2c bus from smallest to largest, X will be [0-4].
In the v4l2-ctl command, use -d /dev/videoX to access different cameras.
In GStreamer, the v4l2src can access different cameras by specifying the device as /dev/videoX.
6.2 gx_probe.sh
By using the gx_probe.sh script, the I²C bus number corresponding to a certain camera, the camera model, width, height, frame rate, etc. can be configured into the environment variables.
In this way, it will facilitate the subsequent use of the media-ctl configuration format, making it easier to operate.
The usage method is:
$ source ./gx_probe.sh i2c_bus
A typical output is as follows:
$ source ./gx_probe.sh 9
Found veye_gxcam camera on i2c-9.
Setenv I2C_BUS = 9
Setenv CAMERAMODEL = GX-MIPI-IMX662
Setenv FPS = 60
Setenv WIDTH = 1920
Setenv HEIGHT = 1080
You can verify the output result of the environment variable by using the command "echo $CAMERAMODEL". Note that this environment variable is only valid for the current session.
7 Real-time preview
7.1 veye_viewer
veye_viewer is an open-source client software based on QT5.
For the code and usage, please refer to:https://github.com/veyeimaging/veye_viewer。
Domestic users can access gitee。
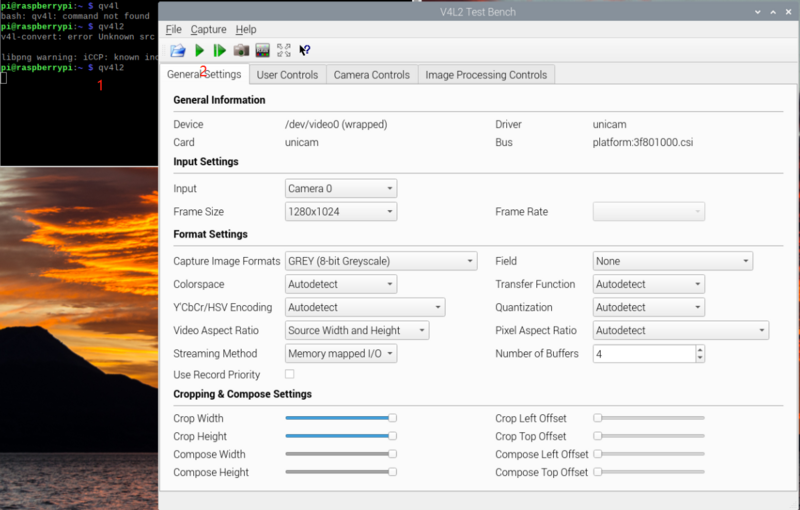
7.2 Use the qv4l2 preview screen
First, install qv4l2
sudo apt install qv4l2
1. Enter "qv4l2" in the command line to start the V4L2 player.
2. Click the ▶ (play) button to bring up the opened media window.
8 Gstreamer Usage
To install the latest accelerated version of gstreamer plugins and applications, please run the following command:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install nvidia-l4t-gstreamer
sudo ldconfig
rm -rf .cache/gstreamer-1.0/
export DISPLAY=:0
- video preview 1080p HD
gst-launch-1.0 nvv4l2camerasrc device=/dev/video0 ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1920, height=(int)1080" ! nvvidconv ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)I420" ! nv3dsink sync=false
gst-launch-1.0 nvv4l2camerasrc device=/dev/video0 ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1920, height=(int)1080" ! nvvidconv ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)NV12" ! nv3dsink sync=false
- video preview 1080p HD(using xvimagesink sink if supported)
export DISPLAY=:0
gst-launch-1.0 -e v4l2src io-mode=4 device=/dev/video0 do-timestamp=true ! 'video/x-raw, width=1920, height=1080, framerate=30/1, format=UYVY' ! xvimagesink sync=false
- Gstreamer is embedded into OpenCV
I think maybe OpenCV do not support I420 data format input,so you should convert it to BGR format.
gst-launch-1.0 nvv4l2camerasrc ! video/x-raw(memory:NVMM), format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1920, height=(int)1080 ! nvvidconv ! video/x-raw(memory:NVMM), format=(string)I420 ! nvvidconv ! video/x-raw, format=(string)BGRx ! videoconvert ! video/x-raw, format=(string)BGR ! appsink
- Video recording 1080p HD
gst-launch-1.0 nvv4l2camerasrc num-buffers=300 ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1920, height=(int)1080" ! nvvidconv ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)NV12" ! nvv4l2h264enc control-rate=1 bitrate=10000000 ! h264parse ! qtmux ! filesink location=filename.mp4 -e
- replay
gst-launch-1.0 filesrc location=filename.mp4 ! qtdemux ! queue ! h264parse ! nvv4l2decoder ! nv3dsink -e
- Snapshots / Photos taken on the spot
gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src num-buffers=1 ! "video/x-raw,format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1920, height=(int)1080" ! nvvidconv ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)I420" ! nvjpegenc ! filesink location=jpgname.jpg
9 yavta(Only supports streaming mode)
9.1 yavta install
git clone https://github.com/veyeimaging/yavta.git
cd yavta;make
Domestic users can access gitee。
9.2 Set image format
v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT,pixelformat=UYVY
9.3 Save the image to a file
9.3.1 under normal conditions
The usual situation here refers to the condition where WIDTH is an integer multiple of 256.
- UYVY type
Take the XAVIER platform as an example
./yavta -c1 -F"uyvy-${WIDTH}x${HEIGHT}.yuv" --skip 0 -f UYVY -s "${WIDTH}x${HEIGHT}" /dev/video0
9.3.2 GX-MIPI-IMX662
./yavta -c1 -Fuyvy-1920x1080.yuv --skip 0 -f UYVY -s 1920x1080 /dev/video0
10 Jetson multimedia-api samples
On the Jetson platform, the Jetson Linux API is provided for developers to use. For the installation of the jetson_multimedia_api package, please refer to the official documentation of NVIDIA.
For the GX series cameras, the ISP function has already been integrated within the camera. Therefore, it is not possible to obtain data using libargus. Instead, data can be directly obtained from the /dev/videoX device file using the standard V4L2 interface.
After installing the Jetson system, you can enter the multimedia API sample directory and compile and run the following command by yourself to preview the camera video:
cd /usr/src/jetson_multimedia_api/samples/12_v4l2_camera_cuda
make
./v4l2_camera_cuda -d /dev/video0 -s 1920x1080 -f UYVY
This command will use the /dev/video0 device for real-time video preview at a resolution of 1920×1080 and in UYVY format.
11 V4L2-CTL Application Examples
11.1 Install v4l2-utils
sudo apt-get install v4l-utils
11.2 Configure parameters using v4l2-ctl
11.2.1 List the data formats supported by the camera
v4l2-ctl --list-formats-ext
Below is an example in the XAVIER system, using the GX-MIPI-IMX662:
ioctl: VIDIOC_ENUM_FMT
Type: Video Capture
[0]: 'UYVY' (UYVY 4:2:2)
Size: Discrete 1920x1080
Interval: Discrete 0.017s (60.000 fps)
[1]: 'YUYV' (YUYV 4:2:2)
[2]: 'NV16' (Y/CbCr 4:2:2)
Size: Discrete 1920x1080
Interval: Discrete 0.017s (60.000 fps)
- Frame rate statistics
v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=1920,height=1080,pixelformat=UYVY --stream-mmap --stream-count=-1 --stream-to=/dev/null
- Save the image to a file
v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=1920,height=1080,pixelformat=UYVY --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=uyvy-1920x1080.yuv
11.2.2 List the configurable parameters of the camera implemented in the driver
v4l2-ctl -L
User Controls
work_mode 0x00981a01 (int) : min=0 max=4 step=1 default=0 value=0 flags=volatile, execute-on-write
trigger_src 0x00981a02 (int) : min=0 max=1 step=1 default=1 value=1 flags=volatile, execute-on-write
soft_trgone 0x00981a03 (button) : flags=write-only, execute-on-write
sync_role 0x00981a04 (int) : min=0 max=1 step=1 default=0 value=0 flags=volatile, execute-on-write
frame_rate 0x00981a05 (int) : min=0 max=60 step=1 default=60 value=60 flags=volatile, execute-on-write
The parameters can be set and retrieved using the following methods.
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl [ctrl_type]=[val]
v4l2-ctl --get-ctrl [ctrl_type]
All of the above functions can be achieved by using the gx_mipi_i2c.sh script.
It should be noted that the above parameters cannot be modified once the image capture process begins. The following will provide detailed explanations for each one:
11.2.3 Configure trigger mode
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl work_mode=[0-2]
0: Streaming Mode
1: Ordinary Trigger Mode
2: Multi-camera Synchronization Mode
11.2.4 Configure trigger source
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl trigger_src=[0-1]
0: Soft Trigger
1: Hard Trigger
11.2.5 Soft trigger once
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl soft_trgone=1
11.2.6 Set frame rate
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl frame_rate=[1-max]
As the resolution is adjusted, the maximum frame rate will be automatically updated.
11.3 stream mode
11.3.1 Set image format
Take the largest screen as an example:
v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT,pixelformat=UYVY
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl frame_rate=$FPS
11.3.2 Frame rate statistics
v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT,pixelformat=UYVY --stream-mmap --stream-count=-1 --stream-to=/dev/null
11.3.3 Save the image to a file
11.3.3.1 under normal conditions
- UYVY
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT,pixelformat=UYVY --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to="uyvy-${WIDTH}x${HEIGHT}.yuv"
11.3.3.2 Use OpenCV to preview images in GREY format
sudo apt install python3-opencv
- We have provided a simple sample to demonstrate how to achieve this functionality:
python3 ./v4l2_opencv_show2.py --width 1920 --height 1080 --fps 60
11.4 Trigger mode
11.4.1 preparatory work
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl low_latency_mode=1
v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT,pixelformat=UYVY
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl frame_rate=$FPS
11.4.2 Soft trigger
11.4.2.1 Setup Mode
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl work_mode=1
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl trigger_src=0
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl vi_time_out_disable=1
11.4.2.2 Start taking pictures
- under normal conditions
The usual situation here refers to the condition where WIDTH is an integer multiple of 256.
v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT,pixelformat=UYVY --stream-mmap --stream-count=-1 --stream-to="uyvy-${WIDTH}x${HEIGHT}.yuv"
- GX-MIPI-IMX662
v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=1920,height=1080,pixelformat=UYVY --stream-mmap --stream-count=-1 --stream-to=uyvy-1920x1080.yuv
11.4.2.3 Perform soft triggering operation
In other shell terminals, you can execute the following command multiple times to trigger it multiple times.
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl soft_trgone=1
11.4.2.4 Stop triggering and collecting
Due to the fact that in the kernel driver, a dead loop is used to wait for new images, it is necessary to first disable vi_time_out_disable, and then exit the acquisition operation.
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl vi_time_out_disable=0
In the terminal of the image acquisition command, press Ctrl+C to exit the acquisition operation.
11.4.3 hardware trigger
To perform the triggering operation using jetson-gpio, first, install and configure jetson-gpio properly.
Next, using Jetson GPIO40 (Board number) as the simulated trigger source and with the rising edge as the trigger condition, an example will be given.
The rich trigger parameter settings can be carried out by using the gx_mipi_i2c.sh script.
11.4.3.1 hardware connection
11.4.3.2 TBD
11.4.3.3 Setup Mode
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl work_mode=1
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl trigger_src=1
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl vi_time_out_disable=1
11.4.3.4 Start taking pictures
- under normal conditions
The usual situation here refers to the condition where WIDTH is an integer multiple of 256.
v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT,pixelformat=UYVY --stream-mmap --stream-count=-1 --stream-to="uyvy-${WIDTH}x${HEIGHT}.yuv"
11.4.3.5 Perform a hard trigger operation
python gpio_trigger_jetson.py
Note:触发脚本链接。
11.4.3.6 Stop triggering and collecting
Due to the fact that in the kernel driver, a dead loop is used to wait for new images, it is necessary to first disable vi_time_out_disable, and then exit the acquisition operation.
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl vi_time_out_disable=0
In the terminal of the image acquisition command, press Ctrl+C to exit the acquisition operation.
11.5 synchronous mode
11.5.1 Set the synchronization mode
$ v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl work_mode=4
11.5.2 Set up the master and slave cameras
Main camera:
$ v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl sync_role=0
slave camera:
$ v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl sync_role=1
11.5.3 Start taking pictures
The method of taking screenshots in the synchronization mode is exactly the same as that in the video stream mode.
12 I2C Script Usage Instructions
We provided shell scripts to configure the parameters.
13 参考资料
14 本文修改记录
- 2025-12-11
第一个发布版本