Difference between revisions of "GX series camera appnotes 4 jetson"
| (23 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [ | + | [[GX series camera appnotes 4 jetson/zh|查看中文]] |
===overview=== | ===overview=== | ||
| − | The GX series cameras are designed for embedded AI applications | + | The GX series cameras are designed for embedded AI applications. They offer high-performance ISP capabilities, support multiple operating modes, provide a wide range of configurable features, and are built with a robust and reliable design. The cameras use the MIPI CSI-2 interface and are well suited for embedded computing platforms. |
This article introduces how to use GX series cameras on the NVIDIA Jetson platform. | This article introduces how to use GX series cameras on the NVIDIA Jetson platform. | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
|GX Series | |GX Series | ||
|GX-MIPI-IMX662 | |GX-MIPI-IMX662 | ||
| − | | | + | |Done |
|} | |} | ||
====Supported Jetson Board==== | ====Supported Jetson Board==== | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
!status | !status | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Xavier NX |
| − | | | + | |Done |
|- | |- | ||
|Orin NX | |Orin NX | ||
| − | | | + | |Done |
|- | |- | ||
|Orin Nano | |Orin Nano | ||
| − | | | + | |Done |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
!FFC line | !FFC line | ||
!Number of cameras | !Number of cameras | ||
| − | ! | + | !Power supply |
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="2" |GX Series | | rowspan="2" |GX Series | ||
| − | | | + | |Xavier NX |
| − | | | + | |15‑pin to 22‑pin FFC (same-side contacts) |
|2 | |2 | ||
| − | |5V DC ( | + | |5V DC (required) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |Orin Nano | + | |Orin Nano,Orin NX |
| − | Orin NX | + | |22‑pin FFC (opposite-side contacts) |
| − | | | ||
|2 | |2 | ||
| − | |5V DC ( | + | |5V DC (required) |
|} | |} | ||
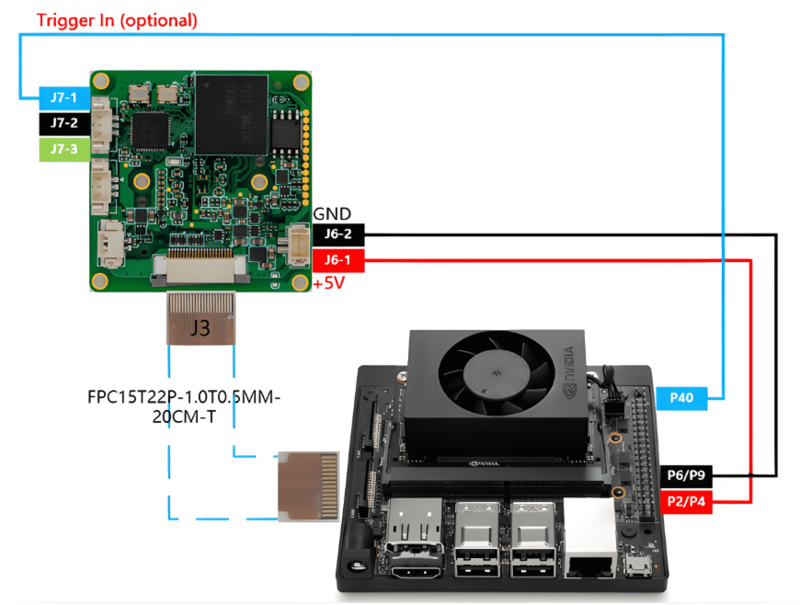
=====GX camera connected to Xavier NX===== | =====GX camera connected to Xavier NX===== | ||
| − | + | <br />[[File:Gx to jetson xavier nx .png|center|thumb|800x800px|GX Camera to Xavier NX]] | |
| + | <br /> | ||
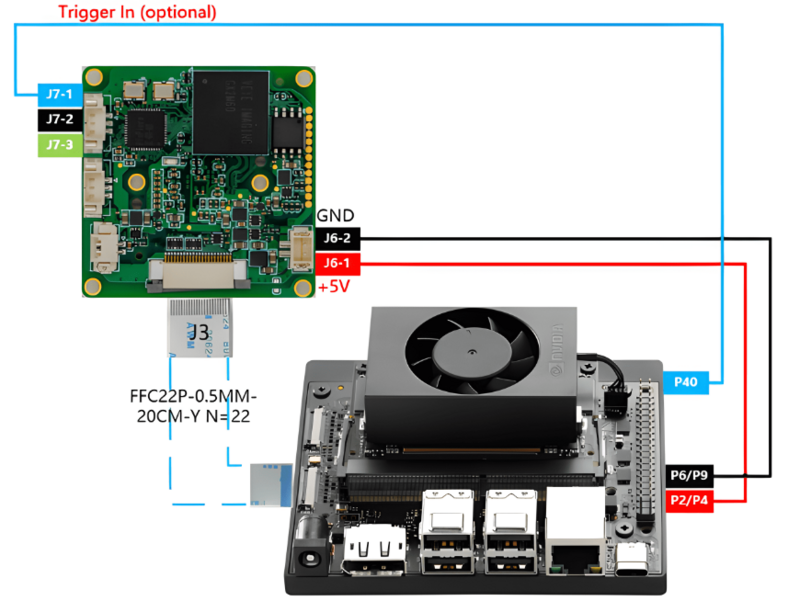
=====The GX camera is connected to Orin Nano or Orin NX.===== | =====The GX camera is connected to Orin Nano or Orin NX.===== | ||
| − | + | <br />[[File:Gx to jetson orin.png|center|thumb|800x800px|GX camera to Orin NX/Nano]] | |
| + | <br /> | ||
===Update the Jetson system=== | ===Update the Jetson system=== | ||
This section describes how to update the L4T system of Jetson to support the GX camera module. For the method of operating system update, please refer to the update instructions for [https://wiki.veye.cc/index.php/How_to_upgrade_the_Jetson_system_to_support_VEYE_cameras/zh Jetson operating system]. | This section describes how to update the L4T system of Jetson to support the GX camera module. For the method of operating system update, please refer to the update instructions for [https://wiki.veye.cc/index.php/How_to_upgrade_the_Jetson_system_to_support_VEYE_cameras/zh Jetson operating system]. | ||
| − | + | Specifically, if trigger functionality is required, the Jetson kernel needs to be patched using '''veye_mv_l4t_<version>.patch'''. | |
| − | This patch | + | This patch provides the following features: |
| − | # | + | #Adds support for monochrome camera data formats '''Y10''' and '''Y12'''. |
| − | # | + | #Adds support for '''trigger mode'''. |
| − | ===Support for | + | ===Support for Trigger Mode === |
| − | The default | + | The default Jetson drivers support only video streaming mode. In the VI driver, data reception includes a timeout mechanism. |
| − | + | We have added a configurable option, '''vi_time_out_disable''', which allows this timeout mechanism to be dynamically enabled or disabled. | |
| − | + | For practical usage, please refer to the example applications provided below. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ===System Status Check === | |
| + | After completing the system update, reboot the Jetson board. | ||
| − | + | During the boot process, the Jetson system will detect any cameras connected to the I²C buses. If a camera is found, the corresponding '''/dev/videoX''' device node will be created. | |
| + | |||
| + | To verify that the camera is correctly connected, run the following command on the Jetson board: | ||
<code>dmesg | grep gxcam</code> | <code>dmesg | grep gxcam</code> | ||
| − | + | The output will display the camera model and version detected during Linux boot. | |
| − | For example, the following | + | For example, the following message indicates that a '''GX-MIPI-IMX662''' camera was detected on '''i2c-9''': |
<code>gxcam 9-003b: camera is: GX-MIPI-IMX662</code> | <code>gxcam 9-003b: camera is: GX-MIPI-IMX662</code> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | ===Status Check and Environment Variable Configuration=== |
| − | + | [https://github.com/veyeimaging/nvidia_jetson_veye_bsp/tree/master/gx_i2c_tools Here], we provide two scripts that can automatically retrieve key information about the connected camera. | |
| − | + | ====probe_camera_info-jetson.sh ==== | |
| + | This script probes connected and successfully probed camera devices, retrieving information such as the video device node and I²C bus. | ||
| − | + | After execution, an '''auto_camera_index.json''' file will be generated in the current directory, containing the retrieved information. | |
| + | |||
| + | Example: | ||
<code>$ ./probe_camera_info-jetson.sh</code> | <code>$ ./probe_camera_info-jetson.sh</code> | ||
| Line 120: | Line 124: | ||
<code>]</code> | <code>]</code> | ||
| − | {} | + | Each <code>{}</code> block represents one camera. If the board supports multiple camera modules, multiple <code>{}</code> blocks will appear in the file. |
The explanation of the camera information is as follows: | The explanation of the camera information is as follows: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| − | |+Camera | + | |+Camera Information |
| − | ! | + | !Field |
| − | ! | + | !Name |
| − | ! | + | !Purpose |
| − | ! | + | !Usage |
|- | |- | ||
|video_node | |video_node | ||
|Video capture device node | |Video capture device node | ||
| − | | | + | |Standard V4L2 video device |
| − | |v4l2-ctl or | + | |Used with <code>v4l2-ctl</code> or customer applications to capture images,and configuring certain camera parameters. |
|- | |- | ||
|i2c_bus | |i2c_bus | ||
| − | |I²C bus | + | |I²C bus |
| − | | | + | |Indicates the I²C bus to which the device is connected |
| − | | | + | |Used as the underlying communication channel for camera parameter configuration, e.g., by the <code>gx_mipi_i2c.sh</code> script |
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | For example, if only one camera is connected, regardless of | + | *The video device nodes and I²C bus numbers used in the following sections can be replaced with the corresponding information obtained from the JSON file generated by the '''probe_camera_info-jetson.sh''' script. |
| + | *On the Jetson system, each camera module is mapped to a <code>/dev/videoX</code> device node. | ||
| + | *During system startup, cameras are probed in ascending order of their I²C bus numbers. The <code>X</code> in <code>/dev/videoX</code> is assigned sequentially starting from 0 according to the probing order. | ||
| + | **For example, if only one camera is connected, <code>X</code> will be 0 regardless of which I²C port the hardware is attached to. | ||
| + | **If five cameras are connected, <code>X</code> values will be <code>[0-4]</code>, ordered by ascending I²C bus numbers. | ||
| + | *In <code>v4l2-ctl</code> commands, the <code>-d /dev/videoX</code> option is used to access different cameras. | ||
| − | In | + | *In GStreamer, <code>v4l2src</code> can access different cameras by specifying <code>device=/dev/videoX</code>. |
| − | |||
====gx_probe.sh==== | ====gx_probe.sh==== | ||
By using the <code>gx_probe.sh</code> script, the I²C bus number corresponding to a certain camera, the camera model, width, height, frame rate, etc. can be configured into the environment variables. | By using the <code>gx_probe.sh</code> script, the I²C bus number corresponding to a certain camera, the camera model, width, height, frame rate, etc. can be configured into the environment variables. | ||
| − | In | + | In that case, subsequent operations using v4l2-ctl will be more convenient. |
The usage method is: | The usage method is: | ||
| Line 176: | Line 179: | ||
<code>Setenv HEIGHT = 1080</code> | <code>Setenv HEIGHT = 1080</code> | ||
| − | You can verify | + | You can verify the environment variable output using, for example: |
| + | |||
| + | <code>echo $CAMERAMODEL</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note: These environment variables are valid only for the current shell session. | ||
===Real-time preview=== | ===Real-time preview=== | ||
====veye_viewer==== | ====veye_viewer==== | ||
| − | veye_viewer is an open-source client | + | The <code>veye_viewer</code> is an open-source, Qt-based client application that allows users to easily evaluate cameras and configure parameters. Its operation logs, register listings, and open-source nature provide a convenient reference for users and support custom development. |
| − | + | The source code of <code>veye_viewer</code> can be downloaded [https://github.com/veyeimaging/veye_viewer here], or platform-specific executable programs are available directly in its [https://github.com/veyeimaging/veye_viewer/releases release packages]. | |
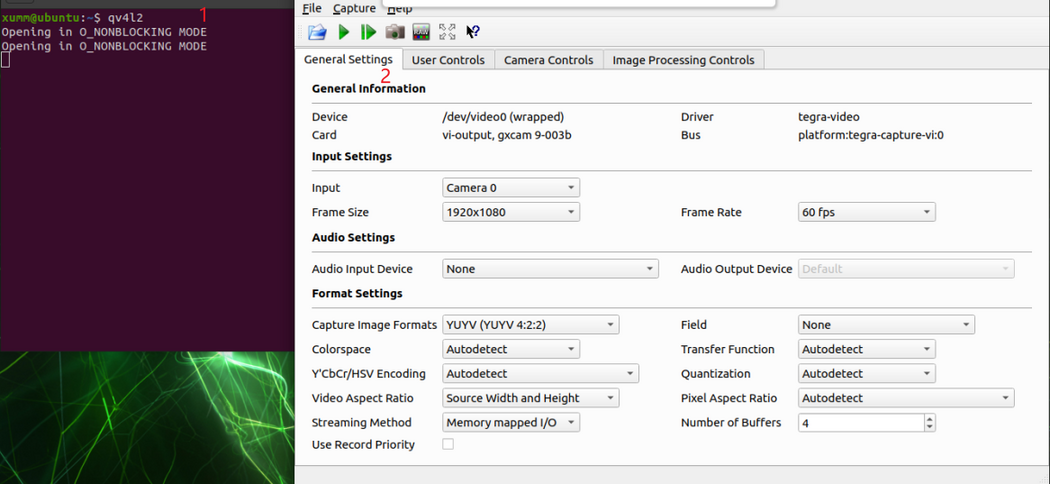
| − | + | ====qv4l2==== | |
| − | ==== | ||
First, install qv4l2 | First, install qv4l2 | ||
| Line 195: | Line 201: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
[[File:Play gx camera using qv4l2.png|center|thumb|1050x1050px|Play gx camera using qv4l2]] | [[File:Play gx camera using qv4l2.png|center|thumb|1050x1050px|Play gx camera using qv4l2]] | ||
| − | + | ||
===Gstreamer Usage=== | ===Gstreamer Usage=== | ||
To install the latest accelerated version of gstreamer plugins and applications, please run the following command: | To install the latest accelerated version of gstreamer plugins and applications, please run the following command: | ||
| Line 231: | Line 237: | ||
<code>gst-launch-1.0 nvv4l2camerasrc num-buffers=300 ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1920, height=(int)1080" ! nvvidconv ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)NV12" ! nvv4l2h264enc control-rate=1 bitrate=10000000 ! h264parse ! qtmux ! filesink location=filename.mp4 -e</code> | <code>gst-launch-1.0 nvv4l2camerasrc num-buffers=300 ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1920, height=(int)1080" ! nvvidconv ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)NV12" ! nvv4l2h264enc control-rate=1 bitrate=10000000 ! h264parse ! qtmux ! filesink location=filename.mp4 -e</code> | ||
| − | * | + | *Playback of saved video file |
<code>gst-launch-1.0 filesrc location=filename.mp4 ! qtdemux ! queue ! h264parse ! nvv4l2decoder ! nv3dsink -e</code> | <code>gst-launch-1.0 filesrc location=filename.mp4 ! qtdemux ! queue ! h264parse ! nvv4l2decoder ! nv3dsink -e</code> | ||
| − | * | + | *Capturing FHD still image |
<code>gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src num-buffers=1 ! "video/x-raw,format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1920, height=(int)1080" ! nvvidconv ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)I420" ! nvjpegenc ! filesink location=jpgname.jpg</code> | <code>gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src num-buffers=1 ! "video/x-raw,format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1920, height=(int)1080" ! nvvidconv ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)I420" ! nvjpegenc ! filesink location=jpgname.jpg</code> | ||
===yavta(Only supports streaming mode)=== | ===yavta(Only supports streaming mode)=== | ||
| − | + | ====yavta install==== | |
<code>git clone <nowiki>https://github.com/veyeimaging/yavta.git</nowiki></code> | <code>git clone <nowiki>https://github.com/veyeimaging/yavta.git</nowiki></code> | ||
<code>cd yavta;make</code> | <code>cd yavta;make</code> | ||
| − | + | ====Set image format==== | |
| − | + | <code>v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT,pixelformat=UYVY</code> | |
| − | + | ====Save the image to a file==== | |
| − | <code>v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT,pixelformat=UYVY</code> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*UYVY type | *UYVY type | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<code>./yavta -c1 -F"uyvy-${WIDTH}x${HEIGHT}.yuv" --skip 0 -f UYVY -s "${WIDTH}x${HEIGHT}" /dev/video0</code> | <code>./yavta -c1 -F"uyvy-${WIDTH}x${HEIGHT}.yuv" --skip 0 -f UYVY -s "${WIDTH}x${HEIGHT}" /dev/video0</code> | ||
| − | + | *GX-MIPI-IMX662 | |
<code>./yavta -c1 -Fuyvy-1920x1080.yuv --skip 0 -f UYVY -s 1920x1080 /dev/video0</code> | <code>./yavta -c1 -Fuyvy-1920x1080.yuv --skip 0 -f UYVY -s 1920x1080 /dev/video0</code> | ||
===Jetson multimedia-api samples=== | ===Jetson multimedia-api samples=== | ||
| − | On the Jetson platform, the [https://docs.nvidia.com/jetson/l4t-multimedia/index.html Jetson Linux API] is provided for developers | + | On the Jetson platform, the [https://docs.nvidia.com/jetson/l4t-multimedia/index.html Jetson Linux API] is provided for developers. For installation of the '''jetson_multimedia_api''' package, please refer to the official NVIDIA documentation. |
| − | For | + | For GX series cameras, ISP functionality is already integrated within the camera module. Therefore, '''libargus''' cannot be used to acquire data. Instead, standard V4L2 interfaces can be used to capture data directly from the <code>/dev/videoX</code> device file. |
| − | After installing the Jetson system, you can | + | After installing the Jetson system, you can navigate to the Multimedia API sample directory, compile, and run the following commands to preview the camera video: |
<code>cd /usr/src/jetson_multimedia_api/samples/12_v4l2_camera_cuda</code> | <code>cd /usr/src/jetson_multimedia_api/samples/12_v4l2_camera_cuda</code> | ||
| Line 276: | Line 275: | ||
<code>./v4l2_camera_cuda -d /dev/video0 -s 1920x1080 -f UYVY</code> | <code>./v4l2_camera_cuda -d /dev/video0 -s 1920x1080 -f UYVY</code> | ||
| − | This command | + | This command uses the <code>/dev/video0</code> device to perform real-time video preview at a resolution of 1920×1080 with the UYVY format. |
| − | === | + | |
| + | ===v4l2-ctl Examples=== | ||
=====Install v4l2-utils===== | =====Install v4l2-utils===== | ||
<code>sudo apt-get install v4l-utils</code> | <code>sudo apt-get install v4l-utils</code> | ||
| Line 285: | Line 285: | ||
<code>v4l2-ctl --list-formats-ext</code> | <code>v4l2-ctl --list-formats-ext</code> | ||
| − | Below is an example | + | Below is an example: |
<code>ioctl: VIDIOC_ENUM_FMT</code> | <code>ioctl: VIDIOC_ENUM_FMT</code> | ||
| Line 334: | Line 334: | ||
<code>v4l2-ctl --get-ctrl [ctrl_type]</code> | <code>v4l2-ctl --get-ctrl [ctrl_type]</code> | ||
| − | All of the above functions can be achieved by using the [ | + | All of the above functions can be achieved by using the [[Gx mipi i2c.sh user guide|gx_mipi_i2c.sh]] script. |
It should be noted that the above parameters cannot be modified once the image capture process begins. The following will provide detailed explanations for each one: | It should be noted that the above parameters cannot be modified once the image capture process begins. The following will provide detailed explanations for each one: | ||
| Line 342: | Line 342: | ||
0: Streaming Mode | 0: Streaming Mode | ||
| − | 1: | + | 1: Trigger Mode |
2: Multi-camera Synchronization Mode | 2: Multi-camera Synchronization Mode | ||
| Line 359: | Line 359: | ||
As the resolution is adjusted, the maximum frame rate will be automatically updated. | As the resolution is adjusted, the maximum frame rate will be automatically updated. | ||
| − | ==== | + | ====Stream mode==== |
=====Set image format===== | =====Set image format===== | ||
| Line 376: | Line 376: | ||
<code>v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT,pixelformat=UYVY --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to="uyvy-${WIDTH}x${HEIGHT}.yuv"</code> | <code>v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT,pixelformat=UYVY --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to="uyvy-${WIDTH}x${HEIGHT}.yuv"</code> | ||
| − | ======Use OpenCV to preview | + | ======Use OpenCV to preview camera====== |
<code>sudo apt install python3-opencv</code> | <code>sudo apt install python3-opencv</code> | ||
| Line 400: | Line 400: | ||
<code>v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl vi_time_out_disable=1</code> | <code>v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl vi_time_out_disable=1</code> | ||
======Start taking pictures====== | ======Start taking pictures====== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<code>v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT,pixelformat=UYVY --stream-mmap --stream-count=-1 --stream-to="uyvy-${WIDTH}x${HEIGHT}.yuv"</code> | <code>v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT,pixelformat=UYVY --stream-mmap --stream-count=-1 --stream-to="uyvy-${WIDTH}x${HEIGHT}.yuv"</code> | ||
| Line 416: | Line 412: | ||
<code>v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl <small>soft_trgone=1</small></code> | <code>v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl <small>soft_trgone=1</small></code> | ||
| − | ======Stop triggering | + | ======Stop triggering====== |
Due to the fact that in the kernel driver, a dead loop is used to wait for new images, it is necessary to first disable vi_time_out_disable, and then exit the acquisition operation. | Due to the fact that in the kernel driver, a dead loop is used to wait for new images, it is necessary to first disable vi_time_out_disable, and then exit the acquisition operation. | ||
| Line 423: | Line 419: | ||
In the terminal of the image acquisition command, press Ctrl+C to exit the acquisition operation. | In the terminal of the image acquisition command, press Ctrl+C to exit the acquisition operation. | ||
| − | ===== | + | =====Hardware trigger===== |
To perform the triggering operation using [https://github.com/NVIDIA/jetson-gpio jetson-gpio], first, install and configure jetson-gpio properly. | To perform the triggering operation using [https://github.com/NVIDIA/jetson-gpio jetson-gpio], first, install and configure jetson-gpio properly. | ||
Next, using Jetson GPIO40 (Board number) as the simulated trigger source and with the rising edge as the trigger condition, an example will be given. | Next, using Jetson GPIO40 (Board number) as the simulated trigger source and with the rising edge as the trigger condition, an example will be given. | ||
| − | The rich trigger parameter settings can be carried out by using the [ | + | The rich trigger parameter settings can be carried out by using the [[Gx mipi i2c.sh user guide|gx_mipi_i2c.sh]] script. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
======Setup Mode====== | ======Setup Mode====== | ||
<code>v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl <small>work_mode=1</small></code> | <code>v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl <small>work_mode=1</small></code> | ||
| Line 440: | Line 433: | ||
<code>v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl vi_time_out_disable=1</code> | <code>v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl vi_time_out_disable=1</code> | ||
======Start taking pictures====== | ======Start taking pictures====== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<code>v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT,pixelformat=UYVY --stream-mmap --stream-count=-1 --stream-to="uyvy-${WIDTH}x${HEIGHT}.yuv"</code> | <code>v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT,pixelformat=UYVY --stream-mmap --stream-count=-1 --stream-to="uyvy-${WIDTH}x${HEIGHT}.yuv"</code> | ||
| Line 449: | Line 438: | ||
<code>python gpio_trigger_jetson.py</code> | <code>python gpio_trigger_jetson.py</code> | ||
| − | Note: | + | Note: Trigger script [https://github.com/veyeimaging/nvidia_jetson_veye_bsp/tree/master/gx_i2c_tools link]. |
======Stop triggering and collecting====== | ======Stop triggering and collecting====== | ||
Due to the fact that in the kernel driver, a dead loop is used to wait for new images, it is necessary to first disable vi_time_out_disable, and then exit the acquisition operation. | Due to the fact that in the kernel driver, a dead loop is used to wait for new images, it is necessary to first disable vi_time_out_disable, and then exit the acquisition operation. | ||
| Line 456: | Line 445: | ||
In the terminal of the image acquisition command, press Ctrl+C to exit the acquisition operation. | In the terminal of the image acquisition command, press Ctrl+C to exit the acquisition operation. | ||
| − | ==== | + | ====Synchronous mode==== |
=====Set the synchronization mode===== | =====Set the synchronization mode===== | ||
| − | <code>$ v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl | + | <code>$ v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-ctrl work_mode=4</code> |
| + | |||
| + | <code>$ v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video1 --set-ctrl work_mode=4</code> | ||
=====Set up the master and slave cameras===== | =====Set up the master and slave cameras===== | ||
Main camera: | Main camera: | ||
| − | <code>$ v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl <small>sync_role=0</small></code> | + | <code>$ v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-ctrl <small>sync_role=0</small></code> |
slave camera: | slave camera: | ||
| − | <code>$ v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl <small>sync_role=1</small></code> | + | <code>$ v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video1 --set-ctrl <small>sync_role=1</small></code> |
=====Start taking pictures===== | =====Start taking pictures===== | ||
| Line 474: | Line 465: | ||
We provided shell scripts to configure the parameters. | We provided shell scripts to configure the parameters. | ||
| − | [ | + | [[gx_mipi_i2c.sh user guide]] |
| − | + | ||
| − | === | + | ===Document Revision History=== |
| − | *2025-12- | + | *2025-12-20 |
| − | + | Initial release. | |
Latest revision as of 14:07, 30 December 2025
1 overview
The GX series cameras are designed for embedded AI applications. They offer high-performance ISP capabilities, support multiple operating modes, provide a wide range of configurable features, and are built with a robust and reliable design. The cameras use the MIPI CSI-2 interface and are well suited for embedded computing platforms.
This article introduces how to use GX series cameras on the NVIDIA Jetson platform.
1.1 Supported camera modules
| series | model | status |
|---|---|---|
| GX Series | GX-MIPI-IMX662 | Done |
1.2 Supported Jetson Board
| Jetson model | status |
|---|---|
| Xavier NX | Done |
| Orin NX | Done |
| Orin Nano | Done |
1.3 Supported L4T versions
- Jetpack5.1.4,L4T version r35.6
- Jetpack6.2.1,L4T version r36.4.4
1.3.1 How to check the current L4T version
On the Jetson board, check the current L4T version and try to replace it with the same version.
cat /etc/nv_tegra_release
As shown:
# R32 (release), REVISION: 7.1......
This indicates that the current L4T version is 32.7.1, and the corresponding Jetpack version is Jetpack 32.6.1.
2 Hardware preparation and installation
The GX series cameras require a adapter board to be connected to the Jetson platform. The supported conditions are as shown in the table below:
| Camera model | Jetson model | FFC line | Number of cameras | Power supply |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GX Series | Xavier NX | 15‑pin to 22‑pin FFC (same-side contacts) | 2 | 5V DC (required) |
| Orin Nano,Orin NX | 22‑pin FFC (opposite-side contacts) | 2 | 5V DC (required) |
2.1 GX camera connected to Xavier NX
2.2 The GX camera is connected to Orin Nano or Orin NX.
3 Update the Jetson system
This section describes how to update the L4T system of Jetson to support the GX camera module. For the method of operating system update, please refer to the update instructions for Jetson operating system.
Specifically, if trigger functionality is required, the Jetson kernel needs to be patched using veye_mv_l4t_<version>.patch.
This patch provides the following features:
- Adds support for monochrome camera data formats Y10 and Y12.
- Adds support for trigger mode.
4 Support for Trigger Mode
The default Jetson drivers support only video streaming mode. In the VI driver, data reception includes a timeout mechanism.
We have added a configurable option, vi_time_out_disable, which allows this timeout mechanism to be dynamically enabled or disabled.
For practical usage, please refer to the example applications provided below.
5 System Status Check
After completing the system update, reboot the Jetson board.
During the boot process, the Jetson system will detect any cameras connected to the I²C buses. If a camera is found, the corresponding /dev/videoX device node will be created.
To verify that the camera is correctly connected, run the following command on the Jetson board:
dmesg | grep gxcam
The output will display the camera model and version detected during Linux boot.
For example, the following message indicates that a GX-MIPI-IMX662 camera was detected on i2c-9:
gxcam 9-003b: camera is: GX-MIPI-IMX662
6 Status Check and Environment Variable Configuration
Here, we provide two scripts that can automatically retrieve key information about the connected camera.
6.1 probe_camera_info-jetson.sh
This script probes connected and successfully probed camera devices, retrieving information such as the video device node and I²C bus.
After execution, an auto_camera_index.json file will be generated in the current directory, containing the retrieved information.
Example:
$ ./probe_camera_info-jetson.sh
cat auto_camera_index.json
[
{"i2c_bus": "9", "video_node": "/dev/video0"}
]
Each {} block represents one camera. If the board supports multiple camera modules, multiple {} blocks will appear in the file.
The explanation of the camera information is as follows:
| Field | Name | Purpose | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| video_node | Video capture device node | Standard V4L2 video device | Used with v4l2-ctl or customer applications to capture images,and configuring certain camera parameters.
|
| i2c_bus | I²C bus | Indicates the I²C bus to which the device is connected | Used as the underlying communication channel for camera parameter configuration, e.g., by the gx_mipi_i2c.sh script
|
- The video device nodes and I²C bus numbers used in the following sections can be replaced with the corresponding information obtained from the JSON file generated by the probe_camera_info-jetson.sh script.
- On the Jetson system, each camera module is mapped to a
/dev/videoXdevice node. - During system startup, cameras are probed in ascending order of their I²C bus numbers. The
Xin/dev/videoXis assigned sequentially starting from 0 according to the probing order.- For example, if only one camera is connected,
Xwill be 0 regardless of which I²C port the hardware is attached to. - If five cameras are connected,
Xvalues will be[0-4], ordered by ascending I²C bus numbers.
- For example, if only one camera is connected,
- In
v4l2-ctlcommands, the-d /dev/videoXoption is used to access different cameras.
- In GStreamer,
v4l2srccan access different cameras by specifyingdevice=/dev/videoX.
6.2 gx_probe.sh
By using the gx_probe.sh script, the I²C bus number corresponding to a certain camera, the camera model, width, height, frame rate, etc. can be configured into the environment variables.
In that case, subsequent operations using v4l2-ctl will be more convenient.
The usage method is:
$ source ./gx_probe.sh i2c_bus
A typical output is as follows:
$ source ./gx_probe.sh 9
Found veye_gxcam camera on i2c-9.
Setenv I2C_BUS = 9
Setenv CAMERAMODEL = GX-MIPI-IMX662
Setenv FPS = 60
Setenv WIDTH = 1920
Setenv HEIGHT = 1080
You can verify the environment variable output using, for example:
echo $CAMERAMODEL
Note: These environment variables are valid only for the current shell session.
7 Real-time preview
7.1 veye_viewer
The veye_viewer is an open-source, Qt-based client application that allows users to easily evaluate cameras and configure parameters. Its operation logs, register listings, and open-source nature provide a convenient reference for users and support custom development.
The source code of veye_viewer can be downloaded here, or platform-specific executable programs are available directly in its release packages.
7.2 qv4l2
First, install qv4l2
sudo apt install qv4l2
1. Enter qv4l2 in the command line to start the V4L2 player.
2. Click the ▶ (play) button to bring up the opened media window.
8 Gstreamer Usage
To install the latest accelerated version of gstreamer plugins and applications, please run the following command:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install nvidia-l4t-gstreamer
sudo ldconfig
rm -rf .cache/gstreamer-1.0/
export DISPLAY=:0
- video preview 1080p HD
gst-launch-1.0 nvv4l2camerasrc device=/dev/video0 ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1920, height=(int)1080" ! nvvidconv ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)I420" ! nv3dsink sync=false
gst-launch-1.0 nvv4l2camerasrc device=/dev/video0 ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1920, height=(int)1080" ! nvvidconv ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)NV12" ! nv3dsink sync=false
- video preview 1080p HD(using xvimagesink sink if supported)
export DISPLAY=:0
gst-launch-1.0 -e v4l2src io-mode=4 device=/dev/video0 do-timestamp=true ! 'video/x-raw, width=1920, height=1080, framerate=30/1, format=UYVY' ! xvimagesink sync=false
- Gstreamer is embedded into OpenCV
I think maybe OpenCV do not support I420 data format input,so you should convert it to BGR format.
gst-launch-1.0 nvv4l2camerasrc ! video/x-raw(memory:NVMM), format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1920, height=(int)1080 ! nvvidconv ! video/x-raw(memory:NVMM), format=(string)I420 ! nvvidconv ! video/x-raw, format=(string)BGRx ! videoconvert ! video/x-raw, format=(string)BGR ! appsink
- Video recording 1080p HD
gst-launch-1.0 nvv4l2camerasrc num-buffers=300 ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1920, height=(int)1080" ! nvvidconv ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)NV12" ! nvv4l2h264enc control-rate=1 bitrate=10000000 ! h264parse ! qtmux ! filesink location=filename.mp4 -e
- Playback of saved video file
gst-launch-1.0 filesrc location=filename.mp4 ! qtdemux ! queue ! h264parse ! nvv4l2decoder ! nv3dsink -e
- Capturing FHD still image
gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src num-buffers=1 ! "video/x-raw,format=(string)UYVY, width=(int)1920, height=(int)1080" ! nvvidconv ! "video/x-raw(memory:NVMM),format=(string)I420" ! nvjpegenc ! filesink location=jpgname.jpg
9 yavta(Only supports streaming mode)
9.1 yavta install
git clone https://github.com/veyeimaging/yavta.git
cd yavta;make
9.2 Set image format
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT,pixelformat=UYVY
9.3 Save the image to a file
- UYVY type
./yavta -c1 -F"uyvy-${WIDTH}x${HEIGHT}.yuv" --skip 0 -f UYVY -s "${WIDTH}x${HEIGHT}" /dev/video0
- GX-MIPI-IMX662
./yavta -c1 -Fuyvy-1920x1080.yuv --skip 0 -f UYVY -s 1920x1080 /dev/video0
10 Jetson multimedia-api samples
On the Jetson platform, the Jetson Linux API is provided for developers. For installation of the jetson_multimedia_api package, please refer to the official NVIDIA documentation.
For GX series cameras, ISP functionality is already integrated within the camera module. Therefore, libargus cannot be used to acquire data. Instead, standard V4L2 interfaces can be used to capture data directly from the /dev/videoX device file.
After installing the Jetson system, you can navigate to the Multimedia API sample directory, compile, and run the following commands to preview the camera video:
cd /usr/src/jetson_multimedia_api/samples/12_v4l2_camera_cuda
make
./v4l2_camera_cuda -d /dev/video0 -s 1920x1080 -f UYVY
This command uses the /dev/video0 device to perform real-time video preview at a resolution of 1920×1080 with the UYVY format.
11 v4l2-ctl Examples
11.1 Install v4l2-utils
sudo apt-get install v4l-utils
11.2 Configure parameters using v4l2-ctl
11.2.1 List the data formats supported by the camera
v4l2-ctl --list-formats-ext
Below is an example:
ioctl: VIDIOC_ENUM_FMT
Type: Video Capture
[0]: 'UYVY' (UYVY 4:2:2)
Size: Discrete 1920x1080
Interval: Discrete 0.017s (60.000 fps)
[1]: 'YUYV' (YUYV 4:2:2)
[2]: 'NV16' (Y/CbCr 4:2:2)
Size: Discrete 1920x1080
Interval: Discrete 0.017s (60.000 fps)
- Frame rate statistics
v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=1920,height=1080,pixelformat=UYVY --stream-mmap --stream-count=-1 --stream-to=/dev/null
- Save the image to a file
v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=1920,height=1080,pixelformat=UYVY --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to=uyvy-1920x1080.yuv
11.2.2 List the configurable parameters of the camera implemented in the driver
v4l2-ctl -L
User Controls
work_mode 0x00981a01 (int) : min=0 max=4 step=1 default=0 value=0 flags=volatile, execute-on-write
trigger_src 0x00981a02 (int) : min=0 max=1 step=1 default=1 value=1 flags=volatile, execute-on-write
soft_trgone 0x00981a03 (button) : flags=write-only, execute-on-write
sync_role 0x00981a04 (int) : min=0 max=1 step=1 default=0 value=0 flags=volatile, execute-on-write
frame_rate 0x00981a05 (int) : min=0 max=60 step=1 default=60 value=60 flags=volatile, execute-on-write
The parameters can be set and retrieved using the following methods.
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl [ctrl_type]=[val]
v4l2-ctl --get-ctrl [ctrl_type]
All of the above functions can be achieved by using the gx_mipi_i2c.sh script.
It should be noted that the above parameters cannot be modified once the image capture process begins. The following will provide detailed explanations for each one:
11.2.3 Configure trigger mode
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl work_mode=[0-2]
0: Streaming Mode
1: Trigger Mode
2: Multi-camera Synchronization Mode
11.2.4 Configure trigger source
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl trigger_src=[0-1]
0: Soft Trigger
1: Hard Trigger
11.2.5 Soft trigger once
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl soft_trgone=1
11.2.6 Set frame rate
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl frame_rate=[1-max]
As the resolution is adjusted, the maximum frame rate will be automatically updated.
11.3 Stream mode
11.3.1 Set image format
Take the largest screen as an example:
v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT,pixelformat=UYVY
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl frame_rate=$FPS
11.3.2 Frame rate statistics
v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT,pixelformat=UYVY --stream-mmap --stream-count=-1 --stream-to=/dev/null
11.3.3 Save the image to a file
11.3.3.1 under normal conditions
- UYVY
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT,pixelformat=UYVY --stream-mmap --stream-count=1 --stream-to="uyvy-${WIDTH}x${HEIGHT}.yuv"
11.3.3.2 Use OpenCV to preview camera
sudo apt install python3-opencv
- We have provided a simple sample to demonstrate how to achieve this functionality:
python3 ./v4l2_opencv_show2.py --width 1920 --height 1080 --fps 60
11.4 Trigger mode
11.4.1 preparatory work
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl low_latency_mode=1
v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT,pixelformat=UYVY
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl frame_rate=$FPS
11.4.2 Soft trigger
11.4.2.1 Setup Mode
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl work_mode=1
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl trigger_src=0
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl vi_time_out_disable=1
11.4.2.2 Start taking pictures
v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT,pixelformat=UYVY --stream-mmap --stream-count=-1 --stream-to="uyvy-${WIDTH}x${HEIGHT}.yuv"
- GX-MIPI-IMX662
v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=1920,height=1080,pixelformat=UYVY --stream-mmap --stream-count=-1 --stream-to=uyvy-1920x1080.yuv
11.4.2.3 Perform soft triggering operation
In other shell terminals, you can execute the following command multiple times to trigger it multiple times.
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl soft_trgone=1
11.4.2.4 Stop triggering
Due to the fact that in the kernel driver, a dead loop is used to wait for new images, it is necessary to first disable vi_time_out_disable, and then exit the acquisition operation.
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl vi_time_out_disable=0
In the terminal of the image acquisition command, press Ctrl+C to exit the acquisition operation.
11.4.3 Hardware trigger
To perform the triggering operation using jetson-gpio, first, install and configure jetson-gpio properly.
Next, using Jetson GPIO40 (Board number) as the simulated trigger source and with the rising edge as the trigger condition, an example will be given.
The rich trigger parameter settings can be carried out by using the gx_mipi_i2c.sh script.
11.4.3.1 Setup Mode
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl work_mode=1
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl trigger_src=1
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl vi_time_out_disable=1
11.4.3.2 Start taking pictures
v4l2-ctl --set-fmt-video=width=$WIDTH,height=$HEIGHT,pixelformat=UYVY --stream-mmap --stream-count=-1 --stream-to="uyvy-${WIDTH}x${HEIGHT}.yuv"
11.4.3.3 Perform a hard trigger operation
python gpio_trigger_jetson.py
Note: Trigger script link.
11.4.3.4 Stop triggering and collecting
Due to the fact that in the kernel driver, a dead loop is used to wait for new images, it is necessary to first disable vi_time_out_disable, and then exit the acquisition operation.
v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl vi_time_out_disable=0
In the terminal of the image acquisition command, press Ctrl+C to exit the acquisition operation.
11.5 Synchronous mode
11.5.1 Set the synchronization mode
$ v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-ctrl work_mode=4
$ v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video1 --set-ctrl work_mode=4
11.5.2 Set up the master and slave cameras
Main camera:
$ v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-ctrl sync_role=0
slave camera:
$ v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video1 --set-ctrl sync_role=1
11.5.3 Start taking pictures
The method of taking screenshots in the synchronization mode is exactly the same as that in the video stream mode.
12 I2C Script Usage Instructions
We provided shell scripts to configure the parameters.
13 Document Revision History
- 2025-12-20
Initial release.