Difference between revisions of "GX Camera on Radxa Boards"
(Created page with "查看中文 ===Overview=== The MV series and RAW series cameras are cameras designed for AI applications in the industrial field. They use t...") |
|||
| (19 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[GX Camera on Radxa Boards/zh|查看中文]] |
===Overview=== | ===Overview=== | ||
| − | The | + | The GX series cameras are cameras designed for AI applications in the industrial field. They use the MIPI CSI-2 interface and are particularly suitable for use with embedded computing platforms. They have rich data formats and triggering features, extremely low latency, high bandwidth, and reliable stability. |
| − | This article takes Radxa's ZERO 3W/3E board as an example to introduce how to connect | + | This article takes Radxa's ZERO 3W/3E board as an example to introduce how to connect GX series cameras to the RK3566/3K3568 system. |
We provide drivers for the Linux operating system (using Radxa OS Debainas an example). | We provide drivers for the Linux operating system (using Radxa OS Debainas an example). | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
!Status | !Status | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |GX series |
| − | | | + | |GX-MIPI-IMX662 |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|Done | |Done | ||
|} | |} | ||
===Hardware Setup=== | ===Hardware Setup=== | ||
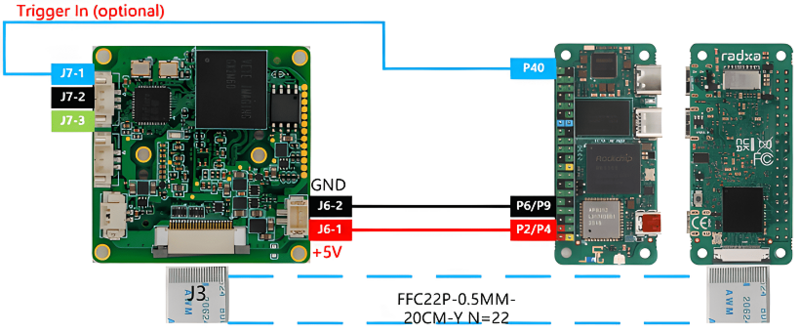
| − | + | ====Connection of other GX series camera and Radxa ZERO 3W/3E==== | |
| − | + | The two are connected using 0.5 mm pitch*22pin FFC cable with opposite-side contacts. The cable must be inserted with the silver contacts facing outside. | |
| − | + | [[File:Gx to radxa resize.png|center|thumb|800x800px|Radxa Zero 3W/3E connect to GX series camera]] | |
| − | + | <br /> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ====Connection of other | ||
| − | The two are connected using 0.5 mm pitch* | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Introduction to github repositories=== | ===Introduction to github repositories=== | ||
| − | |||
https://github.com/veyeimaging/rk35xx_radxa | https://github.com/veyeimaging/rk35xx_radxa | ||
| Line 94: | Line 32: | ||
*application demo | *application demo | ||
| − | In addition, a compiled linux kernel installation package and Android image is provided in the [https://github.com/veyeimaging/ | + | In addition, a compiled linux kernel installation package and Android image is provided in the [https://github.com/veyeimaging/rk35xx_radxa/releases releases]. |
| + | |||
===Upgrade Radxa Debain system=== | ===Upgrade Radxa Debain system=== | ||
====Overview==== | ====Overview==== | ||
| Line 109: | Line 48: | ||
On the RK35xx board, | On the RK35xx board, | ||
| − | Download the latest | + | Download the latest rk356x_radxa_zero3w_gxmcam.tar.gz from [https://github.com/veyeimaging/rk35xx_radxa/releases/ releases]. |
| − | <code>tar -xavf | + | <code>tar -xavf rk356x_radxa_zero3w_gxmcam.tar.gz</code> |
| − | <code>cd | + | <code>cd rk356x_radxa_zero3w_gxmcam</code> |
| − | <code>sudo dpkg -i linux-headers-5.10.160- | + | <code>sudo dpkg -i linux-headers-5.10.160-39-rk356x_5.10.160-39_arm64-gxcam.deb</code> |
| − | <code>sudo dpkg -i linux-image-5.10.160- | + | <code>sudo dpkg -i linux-image-5.10.160-39-rk356x_5.10.160-39_arm64-gxcam.deb</code> |
<code>sudo reboot</code> | <code>sudo reboot</code> | ||
If the version does not match, it needs to be compiled from the source code. | If the version does not match, it needs to be compiled from the source code. | ||
| + | |||
===Check system status=== | ===Check system status=== | ||
====Whether the camera is correctly recognized==== | ====Whether the camera is correctly recognized==== | ||
| Line 128: | Line 68: | ||
Execute the following command on the main board to check if the camera is properly connected. | Execute the following command on the main board to check if the camera is properly connected. | ||
| − | <code>dmesg | grep | + | <code>dmesg | grep gxcam</code> |
You can see the camera model and the camera version number probed. | You can see the camera model and the camera version number probed. | ||
| − | A prompt as below indicates that the | + | A prompt as below indicates that the GX-MIPI-IMX662 camera is detected on the i2c-2 bus. |
| − | <code> | + | <code>gxcam 2-003b: camera is:GX-MIPI-IMX662</code> |
| − | <code> | + | <code>gxcam 2-003b: firmware version: 0x1290133</code> |
For Radxa Zero 3W/3E, the camera is connected to i2c-2. | For Radxa Zero 3W/3E, the camera is connected to i2c-2. | ||
| Line 151: | Line 91: | ||
===Camera Application Development Guide=== | ===Camera Application Development Guide=== | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[GX Camera Application Development Guide|Application Development Guide]] |
===Compile drivers and dtb from source code=== | ===Compile drivers and dtb from source code=== | ||
| Line 158: | Line 98: | ||
https://github.com/veyeimaging/rk35xx_radxa/tree/main/linux/drivers/rk356x | https://github.com/veyeimaging/rk35xx_radxa/tree/main/linux/drivers/rk356x | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===References=== | ===References=== | ||
Latest revision as of 14:42, 23 January 2026
1 Overview
The GX series cameras are cameras designed for AI applications in the industrial field. They use the MIPI CSI-2 interface and are particularly suitable for use with embedded computing platforms. They have rich data formats and triggering features, extremely low latency, high bandwidth, and reliable stability.
This article takes Radxa's ZERO 3W/3E board as an example to introduce how to connect GX series cameras to the RK3566/3K3568 system.
We provide drivers for the Linux operating system (using Radxa OS Debainas an example).
1.1 Camera Module List
| Series | Model | Status |
|---|---|---|
| GX series | GX-MIPI-IMX662 | Done |
2 Hardware Setup
2.1 Connection of other GX series camera and Radxa ZERO 3W/3E
The two are connected using 0.5 mm pitch*22pin FFC cable with opposite-side contacts. The cable must be inserted with the silver contacts facing outside.
3 Introduction to github repositories
https://github.com/veyeimaging/rk35xx_radxa
includes:
- driver source code
- i2c toolkits
- application demo
In addition, a compiled linux kernel installation package and Android image is provided in the releases.
4 Upgrade Radxa Debain system
4.1 Overview
This section describes how to update the RK35xx system to support our camera modules.
We provide a deb installation package that can be installed directly.
4.2 Burn Radxa standard system
Refer to the Radxa documentation to burn in a standard system.
The installation package we are currently releasing is based on this image version.
4.3 Using prebuilt Image and dtb file
Using the compiled debain installation package
On the RK35xx board,
Download the latest rk356x_radxa_zero3w_gxmcam.tar.gz from releases.
tar -xavf rk356x_radxa_zero3w_gxmcam.tar.gz
cd rk356x_radxa_zero3w_gxmcam
sudo dpkg -i linux-headers-5.10.160-39-rk356x_5.10.160-39_arm64-gxcam.deb
sudo dpkg -i linux-image-5.10.160-39-rk356x_5.10.160-39_arm64-gxcam.deb
sudo reboot
If the version does not match, it needs to be compiled from the source code.
5 Check system status
5.1 Whether the camera is correctly recognized
After system update, reboot the main board.
Execute the following command on the main board to check if the camera is properly connected.
dmesg | grep gxcam
You can see the camera model and the camera version number probed.
A prompt as below indicates that the GX-MIPI-IMX662 camera is detected on the i2c-2 bus.
gxcam 2-003b: camera is:GX-MIPI-IMX662
gxcam 2-003b: firmware version: 0x1290133
For Radxa Zero 3W/3E, the camera is connected to i2c-2.
- Check the video0 device node:
ls /dev/video0
You should see:
video0
After successfully identifying the camera, the camera will be recognized as /dev/video0.
6 Camera Application Development Guide
7 Compile drivers and dtb from source code
- RK356x
https://github.com/veyeimaging/rk35xx_radxa/tree/main/linux/drivers/rk356x
8 References
- Radxa Zero 3W/3E Manual
https://docs.radxa.com/zero/zero3
- BSP toolkit
https://radxa-repo.github.io/bsp/
9 Document History
- 2025-12-29
Release 1st version.